Multiple choice Questions of Botany Topic Questions on Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle and Biogeochemical Cycles MCQs ( Questions on Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle and Biogeochemical Cycles Quiz ) for NEET, GATE, AIAPGET, NEET MDS, NEET PG, DNB PDCET, AIIMS SS, PGIMER (Other), AIIMS PG and many more competitive examinations.
Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest Answer Key
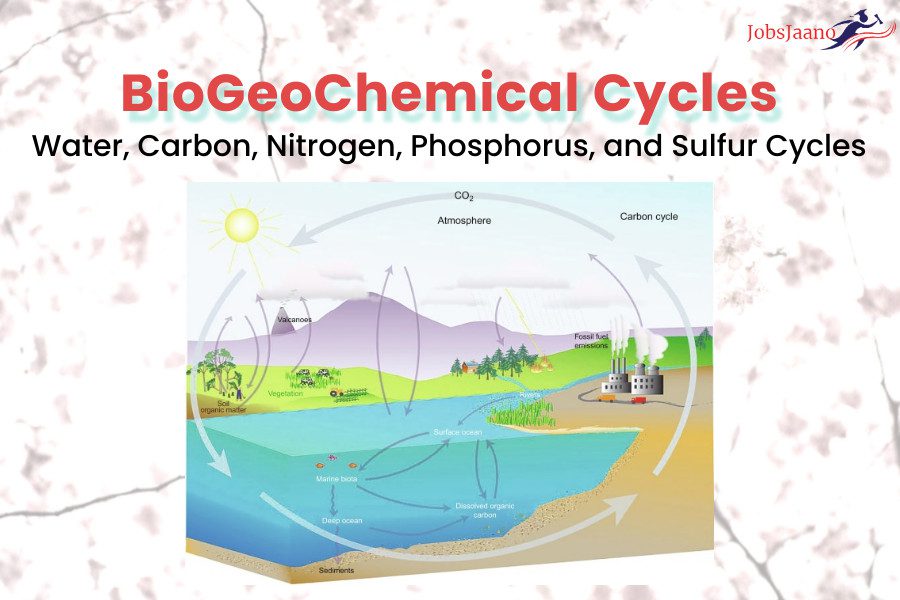
Important Questions of Biogeochemical Cycles including Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur Cycles Multiple Choice Questions for NEET Examination, UPSC Examination, PPSC Examinations.
1. The phosphorus cycle is unusual in that it is entirely
(a) within the aquatic ecosystem
(b) within the terrestrial ecosystem
(c) sedimentary
(d) gaseous
Ans. c
2. Which process converts most carbon from one form to the another?
(a) Animal respiration
(b) Decay
(c) Feeding
(d) Photosynthesis
Ans. d
3. Which of the following atoms typically cycles within the most localised area?
(a) Carbon
(b) Water
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Phosphorus
Ans. d
4. The main nitrogen reservoir in the biosphere is
(a) atmosphere
(b) ocean
(c) organism
(d) rock
Ans. a
5. Which of the following atoms most often limits the primary productivity of an ecosystem?
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Sulphur
(d) Phosphorus
Ans. d
6. The largest reservoir of phosphorus in the biosphere is the
(a) atmosphere
(b) ocean
(c) organisms
(d) rock
Ans. d
7. Most of the earth’s water is
(a) locked up as salt water or ice
(b) stored as carbon dioxide
(c) radioactive
(d) being lost to atmospheric dehydration
Ans. a
Multiple Choice Questions on Biogeochemical Cycles with Answers
8. In the phosphorus cycle, phosphate becomes available by weathering of rock first to
(a) consumers
(b) producers
(c) decomposers
(d) None of these
Ans. c
9. The global hydrologic cycle supports a net flow o atmospheric water vapour from
(a) the oceans to land
(b) land to the oceans
(c) polar to tropical regions
(d) tropical to polar regions
Ans. a
10. Energy and nutrients enter a community by the way of
(a) producer
(b) consumer
(c) scavenger
(d) detritivores
Ans. a
11. Why does after the nutrient enrichment from sewage contamination, a lake often becomes inhospitable to fishes?
(a) Nutrient input, to a lake causes the explosive growth of algal and cyanobacterial populations. This reduces the penetration of light into the lake, the water temperature falls, and eventually the fish population dies
(b) Nutrient input to a lake poisons the fish
(c) Nutrient input to a lake causes the explosive growth of algal and cyanobacterial population. Decomposition of dead algae and cyanobacteria by bacteria results in the depletion of oxygen in the water, which leads to the death of fish
(d) Nutrient input to a lake poisons the organisms that fish eats
Ans. c
12. The phosphorus cycle lacks . component.
(a) an atmospheric
(b) an organic
(c) a mineral
(d) an aquatic
Ans. a
13. Phosphorus cycles absorbs phosphates in the form of
(a) HPO3-
(b) P2(a gas)
(c) PO43-
(d) AIPO4
Ans. c
14. Nitrification is a part of which of the following cycle?
(a) Oxygen cycle
(b) Nitrogen cycle
(c) Phosphorus cycle
(d) None of these
Ans. b
MCQ on Nitrogen Cycle | MCQ on Carbon Cycle | Nitrogen Cycle Questions and Answers pdf
15. Which of the following atoms typically cycles within the most localised area?
(a) Carbon
(b) Water
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Phosphorus
Ans. d
16. What scientific term is used for the circulation of the essential nutrient?
(a) Biogeographic cycle
(b) Cycling of material
(c) Biological cycle
(d) Biogeochemical cycle
Ans. c
17. Which of the following atoms most often limits ue primary productivity of an ecosystem?
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Sulphur
(d) Phosphorus
Ans. a
18. Among the following biogeochemical cycles which one Aes not have losses due to respiration?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Nitrogen
(d) All of these
Ans. d
19. The sedimentary cycle is
(a) oxygen
(b) nitrogen
(c) phosphorus
(d) carbon
Ans. c
20. Sedimentary cycle having a small gaseous component is found in
(a) phosphorus
(b) nitrogen
(c) carbon
(d) sulphur
Ans. d
21. Biogeochemical cycles are also known as
(a) sedimentary cycling
(b) gaseous cycle
(c) material cycling
(d) cycles of water
Ans. c
Nitrogen Fixation MCQ | Nitrogen Metabolism
22. Which of the following organisms can fix nitrogen?
(a) Plants
(b) Fish
(c) Fungi
(d) Bacteria
Ans. d
23. Historically, how did nitrogen enter plants?
(a) Via rocks
(b) As liquid
(c) By bacteria
(d) By snake dung
Ans. c
24. The largest reservoir of phosphours in the biosphere the
(a) atmosphere
(b) ocean 4
(c) organisms
(d) rock
Ans. d
Biogeochemical Cycles | Water Cycles | Carbon Cycles | Nitrogen Cycles | Phosphorus Cycles | Sulfur Cycles
25. Phosphorus cycles in the form of
(a) HPO3-
(b) P2(a gas)
(c) PO42-
(d) AIPO4
Ans. c
26. The phosphorus cycle is unusual in that it is entirely
(a) within the aquatic ecosystem
(b) within the terrestrial ecosystem
(c) sedimentary
(d) gaseous
Ans. c
27. Aquatic ecosystems cover approximately how much of the earth’s surface?
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 75%
(d) 90%
Ans. c
28. Which of the following atoms typically cycles within the most localised area?
(a) Carbon
(b) Water
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Phosphorus
Ans. d
29. Nitrogen is a critical elements of the ecosystem because it is
(a) essential element
(b) abundant in atmosphere
(c) labile
(d) fixed by microbes
Ans. a
30. Which one is sedimentary cycle?
(a) Oxygen cycle
(b) Nitrogen cycle
(c) Hydrogen cycle
(d) None of these
Ans. d
For More Topic Wise Botany MCQs CLICK HERE
For Zoology MCQs CLICK HERE
For Environment and Ecology MCQs Click Here
Related Queries: