Multiple choice Questions of Botany Topic Plant Tissue Culture MCQ and Structure, Development & Types of Endosperm MCQs with Answers ( Plant Tissue Culture MCQ and Structure, Development & Types of Endosperm Quiz ) for NEET, GATE, AIAPGET, NEET MDS, NEET PG, DNB PDCET, AIIMS SS, PGIMER (Other), AIIMS PG and many more competitive examinations.
Plant Tissue Culture MCQ
1. The ploidy level of endosperm is
( a ) haploid
( b ) diploid
( c ) triploid
( d ) None of these
Ans. c
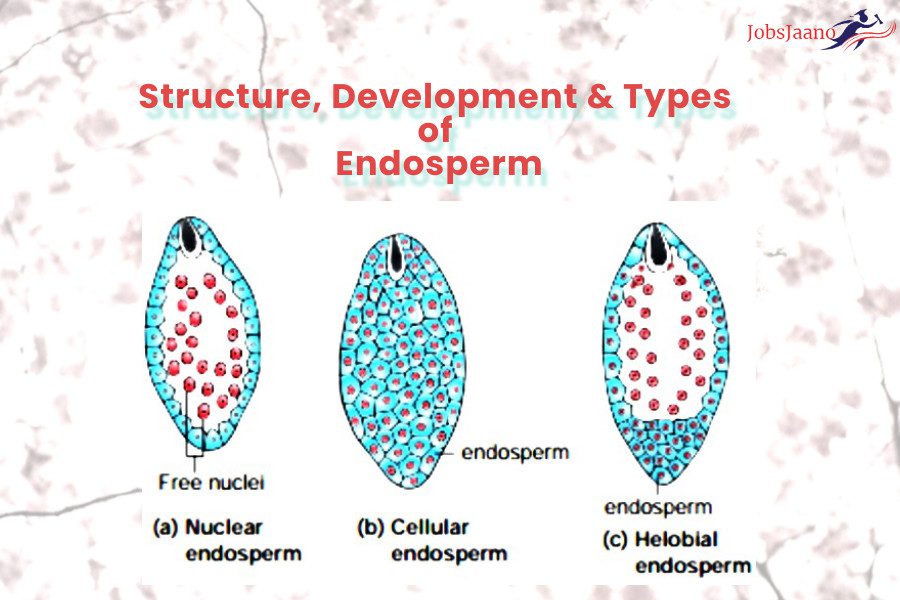
2. Major types of endosperms are
( a ) 2
( b ) 3
( c ) 6
( d ) 8
Ans. b
3. Which of the following types of endosperm is found in 25 % of angiosperms ?
( a ) Cellular
( b ) Nuclear
( c ) Helobial
( d ) All of these
Ans. a
4. During nuclear type of endosperm development , primary endosperm mother cell divide by
( a ) mitosis
( b ) meiosis
( c ) free nuclear division
( d ) Both ( a ) and ( b )
Ans. c
5. Which of the following types of endosperm is found in Datura ?
( a ) Nuclear
( b ) Cellular
( c ) Helobial
( d ) None of these
Ans. c
6. Acer , Lomatia and Calotropis have which of the following ?
( a ) Cellular
( b ) Nuclear
( c ) Helobial
( d ) Both ( b ) and ( c )
Ans. b
7. Which of the following type of endosperm is common in monocots ?
( a ) Helobial
( b ) Cellular
( c ) Nuclear
( d ) None of these
Ans. a
8. In cereals , the cells of the outermost layer of the endosperm becomes morphologically and physiologically specialised and form a layer of cells called
( a ) perisperm
( b ) tapetum
( c ) aleurone layer
( d ) All of these
Ans. c
9. Asphodelus shows which type of endosperm ?
( a ) Cellular
( b ) Nuclear
( c ) Helobial
( d ) None of these
Ans. c
10. In nuclear division , the nuclei after free division arranged themselves towards ….. of embryo sac .
( a ) center
( b ) periphery
( c ) Both ( a ) and ( b )
( d ) None of these
Ans. b
mcq on plant tissue culture
11. Milky water of green coconut is liquid
( a ) nucellus
( b ) of female gametophyte
( c ) endosperm
( d ) chalaza
Ans. c
12. The aleurone layer of endosperm in monocot seed is related to
( a ) growth of endosperm
( b ) digestion of reserve food of endosperm
( c ) store the food of endosperm
( d ) formation of endosperm
Ans. b
13. Nuclear endosperm is found in which of the following ?
( a ) Adoxa
( b ) Datura
( c ) Citrus
( d ) Asphodelus
Ans. c
14. Endosperm of angiosperms is produced after the fertilisation of male gamete with
( a ) synergids
( b ) secondary nucleus
( c ) ospore
( d ) antipodals
Ans. b
Angiosperms mcq pdf | plant tissue culture mcq question bank | mcq on protoplast culture
15. In Oenothera , the ploidy level of endosperm is
( a ) 2n
( b ) 3n
( c ) 4n
( d ) n
Ans. a
16. Double fertilisation in angiosperms results in the formation of
( a ) embryo
( b ) endosperm
( c ) Both ( a ) and ( b )
( d ) None of these
Ans. c
17. Double fertilisation in angiosperm was discovered by whom ?
( a ) Nawaschin
( b ) Nageli
( c ) Darwin
( d ) None of these
Ans. a
18. Development of an endosperm occurs in
( a ) pollen sac
( b ) ovule
( c ) embryo sac
( d ) locule
Ans. c
19. Three types of endosperm are cellular , nuclear and
( a ) celluloid
( b ) helobial
( c ) Both ( a ) and ( b )
( d ) All of these
Ans. b
20. Which of the following is an intermediate type of endosperm ?
( a ) Cellular
( b ) Nuclear
( c ) Helobial
( d ) None of the above
Ans. c
Plant Tissue Culture MCQ with Answers pdf | Plant Cell Culture
21. An endosperm having irregular boundaries is termed as
( a ) nuclear
(b) cellular
( c ) helobial
( d ) ruminate
Ans. d
22. Endosperm is generally
( a ) diploid
( b ) triploid
( c ) haploid
( d ) polyploid
Ans. b
23. The maximum ploidy seen in the secondary nucleus is
( a ) 7n
( b ) 14n
( c ) 15n
( d ) 10n
Ans. b
24. The term Xenia denotes the effect of pollen on the
( a ) endosperm
( b ) egg
( c ) nucellus
( d ) seed coat
Ans. a
25. Endosperm in angiosperms results after fertilisation form
( a ) zygote
( b ) secondary nucleus
( c ) antipodals
( d ) synergids
Ans. b
MCQ on Seed Dormancy | Plant tissue culture multiple choice questions | Megasporogenesis
26. Aleurone layer is present in
( a ) the peripheral part of endosperm
( b ) the peripheral part of scutellum
( c ) the peripheral part of coleoptile
( d ) the peripheral part of cotyledons
Ans. a
27. The aleurone layer of endosperm in monocot seed is related to
( a ) growth of endosperm
( b ) digestion of reserve food of embryo
( c ) store the food of endosperm
( d ) formation of endosperm
Ans. b
28. In which of the following helobial endosperm occurs ?
( a ) Acalypha
( b ) Cocos
( c ) Cannabis
( d ) Adoxa
Ans. b
29. The structure which can show the effect of traits brought by the male gamete immediately after its formation is
( a ) embryo
( b ) cotyledons
( c ) endosperm
( d ) plumule
Ans. c
30. Free nuclear divisions are characteristic of
( a ) cellular endosperm
( b ) nuclear endosperm
( c ) helobial endosperm
( d ) Both ( b ) and ( c )
Ans. d
For More Topic Wise Botany MCQs CLICK HERE
For Zoology MCQs CLICK HERE
For Environment and Ecology MCQs Click Here
Related Queries: