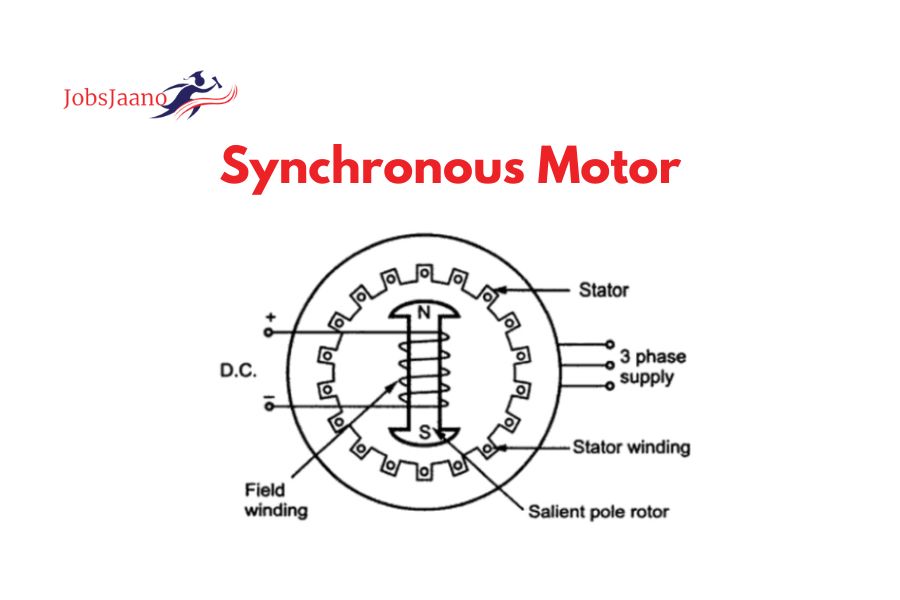
Synchronous Motor PDF | MCQs on Synchronous Motor: Synchronous motors are a type of electric motor that operate at a fixed speed determined by the frequency of the power supply. They are called “synchronous” because the speed of the motor is synchronized with the frequency of the alternating current (AC) power supply.
Here are some key features and characteristics of synchronous motors:
- Construction: Synchronous motors consist of a rotor and a stator. The rotor contains field windings, which are energized with direct current (DC) to create a magnetic field. The stator has armature windings that are connected to the power supply.
- Synchronization: The rotational speed of synchronous motors is determined by the frequency of the AC power supply and the number of poles in the motor. The number of poles corresponds to the number of pairs of magnetic poles in the rotor. For example, a motor with four poles will have two pairs of magnetic poles.
- Stator Excitation: Synchronous motors require a separate DC power source to energize the field windings on the rotor. This excitation creates a constant magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field produced by the stator windings. The interaction between the two fields creates the torque that drives the motor.
- Power Factor Correction: One of the significant advantages of synchronous motors is their ability to provide power factor correction. They can operate at a leading power factor, which helps to reduce the reactive power and improve the overall efficiency of the electrical system.
- Applications: Synchronous motors are commonly used in industrial applications where a constant speed is required, such as large compressors, pumps, fans, and mills. They are also used in power generation systems, including hydroelectric plants, thermal power stations, and wind turbines.
- Control and Starting: Synchronous motors require a specialized control system to synchronize their speed with the power supply frequency. They also need external starting mechanisms such as a motor starting capacitor or a starting motor to bring them up to synchronous speed before they can be synchronized.
It’s worth noting that there are different types of synchronous motors, including synchronous reluctance motors and permanent magnet synchronous motors, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Synchronous Machine PDF | Synchronous Phase Modifier Quiz
1. What determines the speed of a synchronous motor?
a) Voltage of the power supply
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Number of stator windings
d) Size of the rotor
Answer: b) Frequency of the power supply
2. What is the purpose of field windings in a synchronous motor?
a) To generate the magnetic field on the stator
b) To convert AC power to DC power
c) To provide power factor correction
d) To create the magnetic field on the rotor
Answer: d) To create the magnetic field on the rotor
3. Which of the following statements about synchronous motors is true?
a) They can operate at variable speeds.
b) They do not require any power supply.
c) They operate at a speed determined by the frequency of the power supply.
d) They are only used in small-scale applications.
Answer: c) They operate at a speed determined by the frequency of the power supply.
4. Synchronous motors are commonly used in which of the following applications?
a) Residential air conditioning units
b) Electric vehicles
c) Industrial pumps and compressors
d) Portable electronic devices
Answer: c) Industrial pumps and compressors
5. Which type of synchronous motor provides power factor correction?
a) Synchronous reluctance motor
b) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
c) Brushless DC motor
d) All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
6. Which of the following is an advantage of synchronous motors?
a) High starting torque
b) Variable speed operation
c) Low cost
d) Power factor correction
Answer: d) Power factor correction
7. Synchronous motors require separate excitation for their operation. What does this mean?
a) They are powered by a separate battery.
b) They require an external power supply to energize the rotor field windings.
c) They need a constant supply of lubrication.
d) They have additional safety features.
Answer: b) They require an external power supply to energize the rotor field windings.
8. The synchronous speed of a four-pole synchronous motor connected to a 50 Hz power supply is:
a) 750 RPM
b) 1500 RPM
c) 3000 RPM
d) 6000 RPM
Answer: b) 1500 RPM
9. What happens if the rotor of a synchronous motor falls out of synchronization with the power supply frequency?
a) The motor operates at a higher speed.
b) The motor operates at a lower speed.
c) The motor stops running.
d) The motor continues to run at the same speed.
Answer: c) The motor stops running.
10. In a synchronous motor, the power factor is leading when:
a) The motor is operating at full load.
b) The motor is under-excited.
c) The motor is over-excited.
d) The motor is at no-load condition.
Answer: c) The motor is over-excited.
11. Which type of synchronous motor does not require any external excitation?
a) Brushless DC motor
b) Synchronous reluctance motor
c) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
d) Salient pole synchronous motor
Answer: c) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
12. Which component of a synchronous motor is responsible for providing mechanical output power?
a) Stator
b) Rotor
c) Field windings
d) Armature windings
Answer: b) Rotor
13. Synchronous motors are not suitable for applications requiring variable speed control because:
a) They have fixed speed characteristics.
b) They have low torque output.
c) They are expensive.
d) They are difficult to maintain.
Answer: a) They have fixed speed characteristics.
14. Which of the following factors affect the torque production of a synchronous motor?
a) Power factor
b) Magnetic field strength
c) Number of stator windings
d) Size of the motor enclosure
Answer: b) Magnetic field strength
15. The efficiency of a synchronous motor is highest when it operates at:
a) Full load
b) No load
c) Half load
d) Overload
Answer: a) Full load
16. Which type of motor does not require any external power source to create a rotating magnetic field?
a) Synchronous motor
b) Induction motor
c) DC motor
d) Stepper motor
Answer: b) Induction motor
17. In a synchronous motor, the stator magnetic field is created by:
a) Permanent magnets
b) Stator windings
c) Rotor windings
d) External power supply
Answer: b) Stator windings
18. The synchronous speed of a six-pole synchronous motor connected to a 60 Hz power supply is:
a) 600 RPM
b) 900 RPM
c) 1800 RPM
d) 3600 RPM
Answer: c) 1800 RPM
19. What happens if the load on a synchronous motor exceeds its rated torque?
a) The motor slows down
b) The motor speeds up
c) The motor stalls
d) The motor reverses its direction
Answer: c) The motor stalls
20. Synchronous motors are typically more efficient than induction motors at:
a) Low loads
b) High loads
c) No load
d) Variable loads
Answer: b) High loads
Working principle of synchronous motor pdf | Synchronous generators pdf
21. Which type of synchronous motor has a rotor with salient poles?
a) Hysteresis motor
b) Reluctance motor
c) Permanent magnet motor
d) Salient pole motor
Answer: d) Salient pole motor
22. In a synchronous motor, hunting refers to:
a) Oscillations in motor speed
b) Noise produced during operation
c) Vibrations in the motor structure
d) Overheating of the motor windings
Answer: a) Oscillations in motor speed
23. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications that require:
a) High starting torque
b) Variable speed control
c) Low power factor
d) Precise speed synchronization
Answer: d) Precise speed synchronization
24. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted by varying the:
a) Load torque
b) Supply voltage
c) Rotor speed
d) Field excitation current
Answer: d) Field excitation current
25. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in small household appliances like fans and washing machines?
a) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
b) Reluctance synchronous motor
c) Hysteresis synchronous motor
d) Salient pole synchronous motor
Answer: a) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
26. Which of the following is not a type of synchronous motor?
a) Brushless DC motor
b) Reluctance motor
c) Stepper motor
d) Induction motor
Answer: d) Induction motor
27. What is the primary advantage of a synchronous motor over an induction motor?
a) Higher efficiency
b) Lower cost
c) Easier maintenance
d) Variable speed operation
Answer: a) Higher efficiency
28. Which component of a synchronous motor is responsible for producing the rotating magnetic field?
a) Stator windings
b) Rotor windings
c) Field windings
d) Armature windings
Answer: c) Field windings
29. The rotor of a synchronous motor is locked to the rotating magnetic field, resulting in:
a) Slip
b) Synchronous speed
c) Variable speed
d) Reduced torque
Answer: b) Synchronous speed
30. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted by changing the:
a) Voltage supply
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Number of stator windings
d) Excitation current
Answer: d) Excitation current
31. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications that require precise:
a) Torque control
b) Speed control
c) Power factor correction
d) Voltage regulation
Answer: b) Speed control
32. Which type of synchronous motor uses permanent magnets in the rotor?
a) Brushless DC motor
b) Reluctance motor
c) Salient pole motor
d) Hysteresis motor
Answer: a) Brushless DC motor
33. What is the primary drawback of a synchronous motor?
a) High cost
b) Low efficiency
c) Complex control requirements
d) Limited operating speed range
Answer: c) Complex control requirements
34. Synchronous motors are more commonly used in which power range?
a) Low power applications
b) Medium power applications
c) High power applications
d) All power ranges equally
Answer: c) High power applications
35. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a synchronous motor?
a) Fixed speed
b) Low starting torque
c) Power factor correction
d) High efficiency
Answer: b) Low starting torque
36. Which of the following is not a method for starting a synchronous motor?
a) Direct-on-line (DOL) starting
b) Auto-transformer starting
c) Star-delta starting
d) Stator resistance starting
Answer: d) Stator resistance starting
37. Synchronous motors are known for their constant speed because:
a) They have a fixed number of poles
b) They use permanent magnets in the rotor
c) They operate at a fixed frequency
d) They have a variable speed controller
Answer: c) They operate at a fixed frequency
38. What happens to the power factor of a synchronous motor when it operates at a leading power factor?
a) It improves the overall system power factor
b) It reduces the overall system power factor
c) It has no effect on the overall system power factor
d) It results in a lagging power factor in the system
Answer: a) It improves the overall system power factor
39. Which of the following is a disadvantage of synchronous motors compared to induction motors?
a) Lower efficiency
b) Higher cost
c) Limited torque output
d) Inability to operate at low speeds
Answer: b) Higher cost
Permanent magnet synchronous motor pdf | synchronous motor mcq
40. In a synchronous motor, if the rotor falls out of synchronization with the stator field, what is the term used to describe this condition?
a) Stalling
b) Cogging
c) Hunting
d) Slipping
Answer: c) Hunting
41. The torque produced in a synchronous motor is directly proportional to the:
a) Voltage applied to the stator
b) Current flowing through the rotor windings
c) Power factor of the motor
d) Excitation current of the rotor
Answer: d) Excitation current of the rotor
42. Which of the following factors does not affect the synchronous speed of a motor?
a) Number of stator poles
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Number of rotor poles
d) Diameter of the rotor
Answer: d) Diameter of the rotor
43. Synchronous motors are often used in applications that require:
a) High torque at low speeds
b) Variable speed control
c) Low power factor
d) Compact size and lightweight
Answer: b) Variable speed control
44. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in large power generation plants?
a) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
b) Hysteresis synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) Reluctance synchronous motor
Answer: c) Salient pole synchronous motor
45. The speed of a synchronous motor is directly proportional to the:
a) Number of rotor poles
b) Number of stator poles
c) Rated voltage of the motor
d) Applied load torque
Answer: b) Number of stator poles
46. Which of the following is a common method used to control the speed of a synchronous motor?
a) Changing the number of stator windings
b) Varying the excitation current
c) Adjusting the rotor resistance
d) Modifying the power supply frequency
Answer: d) Modifying the power supply frequency
47. Synchronous motors are known for their high:
a) Starting torque
b) Efficiency
c) Slip
d) Power factor
Answer: d) Power factor
48. Which type of synchronous motor does not require any separate excitation?
a) Salient pole synchronous motor
b) Reluctance synchronous motor
c) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
d) Hysteresis synchronous motor
Answer: c) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
49. The maximum torque that a synchronous motor can produce is limited by its:
a) Rotor size
b) Stator size
c) Excitation current
d) Operating frequency
Answer: c) Excitation current
50. What happens to the power factor of a synchronous motor when it operates at a lagging power factor?
a) It improves the overall system power factor
b) It reduces the overall system power factor
c) It has no effect on the overall system power factor
d) It results in a leading power factor in the system
Answer: b) It reduces the overall system power factor
Synchronous motors are mcq | synchronous machine numerical questions
51. Synchronous motors are often used in applications where precise synchronization is required, such as:
a) Electric vehicles
b) Air compressors
c) Printing presses
d) Ceiling fans
Answer: c) Printing presses
52. Which of the following types of synchronous motors is self-starting?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Reluctance synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) None of the above
Answer: d) None of the above
53. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted by changing the:
a) Rotor size
b) Stator size
c) Excitation current
d) Number of stator windings
Answer: c) Excitation current
54. Which of the following is a disadvantage of permanent magnet synchronous motors?
a) High cost of permanent magnets
b) Limited operating temperature range
c) Low efficiency
d) Difficulties in controlling the speed
Answer: a) High cost of permanent magnets
55. Synchronous motors are not suitable for applications that require:
a) High starting torque
b) Precise speed control
c) Low power consumption
d) Variable speed operation
Answer: d) Variable speed operation
56. Which of the following is an advantage of a brushless synchronous motor over a brushed synchronous motor?
a) Higher torque output
b) Lower cost
c) Reduced maintenance
d) Simpler control circuitry
Answer: c) Reduced maintenance
57. Synchronous motors are commonly used in which industrial application?
a) Electric vehicles
b) HVAC systems
c) Robotics
d) Household appliances
Answer: c) Robotics
58. The synchronous speed of a synchronous motor is determined by:
a) The number of rotor poles
b) The number of stator poles
c) The applied load torque
d) The motor’s power rating
Answer: b) The number of stator poles
59. Which type of synchronous motor is known for its smooth operation and constant speed?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
c) Reluctance synchronous motor
d) Salient pole synchronous motor
Answer: a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
60. In a synchronous motor, if the rotor speed exceeds the synchronous speed, it is known as:
a) Slipping
b) Cogging
c) Hunting
d) Stalling
Answer: c) Hunting
pmsm motor datasheet
61. Which of the following factors affects the torque production of a synchronous motor?
a) Stator resistance
b) Rotor diameter
c) Number of stator windings
d) Excitation current
Answer: d) Excitation current
62. Which component of a synchronous motor provides mechanical power output?
a) Stator
b) Rotor
c) Field windings
d) Armature windings
Answer: b) Rotor
63. The power factor of a synchronous motor is unity when:
a) The motor is operating at full load
b) The motor is under-excited
c) The motor is over-excited
d) The motor is at no-load condition
Answer: c) The motor is over-excited
64. What happens to the power factor of a synchronous motor when it operates at full load?
a) It decreases
b) It increases
c) It remains the same
d) It cannot be determined
Answer: b) It increases
65. Which of the following methods is commonly used to start a large synchronous motor?
a) Direct-on-line (DOL) starting
b) Star-delta starting
c) Auto-transformer starting
d) Variable frequency drive (VFD) starting
Answer: c) Auto-transformer starting
66. Which of the following statements is true regarding the excitation of a synchronous motor?
a) Synchronous motors do not require any excitation.
b) Synchronous motors are self-excited.
c) Synchronous motors require external excitation.
d) Synchronous motors use permanent magnets for excitation.
Answer: c) Synchronous motors require external excitation.
67. What is the primary purpose of damper windings in a synchronous motor?
a) To improve the power factor
b) To reduce the rotor losses
c) To provide mechanical damping
d) To increase the torque output
Answer: c) To provide mechanical damping
68. Which of the following factors affects the torque-angle characteristics of a synchronous motor?
a) Supply voltage
b) Stator resistance
c) Load torque
d) Excitation current
Answer: d) Excitation current
69. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in applications that require high torque at low speeds?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Salient pole synchronous motor
c) Reluctance synchronous motor
d) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
Answer: b) Salient pole synchronous motor
70. The field excitation in a synchronous motor is adjusted to control the:
a) Power factor
b) Speed
c) Torque
d) Efficiency
Answer: a) Power factor
Synchronous reluctance motor pdf | Application of synchronous motor pdf
71. Synchronous motors are known for their ability to maintain a constant:
a) Power factor
b) Speed
c) Torque
d) Voltage
Answer: b) Speed
72. Which of the following is an application where synchronous motors are commonly used?
a) Home appliances
b) Electric vehicles
c) Personal computers
d) Ceiling fans
Answer: b) Electric vehicles
73. Which of the following types of synchronous motors has a rotor with non-magnetic material?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) Reluctance synchronous motor
Answer: d) Reluctance synchronous motor
74. What happens to the torque production of a synchronous motor when it operates at a leading power factor?
a) Torque decreases
b) Torque increases
c) Torque remains the same
d) Torque cannot be determined
Answer: a) Torque decreases
75. The maximum torque that a synchronous motor can produce is directly proportional to the:
a) Supply voltage
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Excitation current
d) Load torque
Answer: c) Excitation current
76. Which of the following is an advantage of a synchronous motor over an induction motor?
a) Lower cost
b) Higher starting torque
c) Constant speed operation
d) Lower maintenance requirements
Answer: c) Constant speed operation
77. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications that require:
a) Variable speed control
b) High starting torque
c) Low power factor
d) Simple control circuitry
Answer: a) Variable speed control
78. The stator windings of a synchronous motor are typically connected to:
a) A three-phase power supply
b) A single-phase power supply
c) A DC power supply
d) A variable frequency power supply
Answer: a) A three-phase power supply
79. Which of the following factors does not affect the synchronous speed of a motor?
a) Number of rotor poles
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Number of stator poles
d) Rated voltage of the motor
Answer: d) Rated voltage of the motor
80. Synchronous motors are generally not self-starting because they lack:
a) Rotor windings
b) Field windings
c) Armature windings
d) Starting torque
Answer: d) Starting torque
types of synchronous motor pdf | synchronous and asynchronous machines pdf
81. Which type of synchronous motor has a rotor with permanent magnets?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Reluctance synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
Answer: d) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
82. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted by changing the:
a) Rotor size
b) Stator size
c) Excitation current
d) Number of stator windings
Answer: c) Excitation current
83. Synchronous motors are commonly used in power systems for:
a) Voltage regulation
b) Current overload protection
c) Power factor correction
d) Harmonic filtering
Answer: c) Power factor correction
84. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in applications that require high precision and stability?
a) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
b) Hysteresis synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) Reluctance synchronous motor
Answer: b) Hysteresis synchronous motor
85. In a synchronous motor, the torque developed is proportional to the:
a) Square of the stator current
b) Square of the rotor current
c) Product of stator and rotor currents
d) Difference between stator and rotor currents
Answer: c) Product of stator and rotor currents
86. In a synchronous motor, the rotor rotates at a speed equal to:
a) The synchronous speed
b) The slip speed
c) The rated speed
d) The rotor winding speed
Answer: a) The synchronous speed
87. Which of the following methods is commonly used to control the torque output of a synchronous motor?
a) Varying the stator voltage
b) Adjusting the rotor resistance
c) Changing the number of stator windings
d) Modifying the excitation current
Answer: d) Modifying the excitation current
88. Which of the following is a characteristic of a hysteresis synchronous motor?
a) High starting torque
b) Constant speed operation
c) Self-starting capability
d) High efficiency
Answer: b) Constant speed operation
89. What is the main advantage of a reluctance synchronous motor?
a) High efficiency
b) Variable speed operation
c) Low cost
d) High power factor
Answer: c) Low cost
90. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be improved by:
a) Adding external resistance in the rotor circuit
b) Adjusting the number of stator windings
c) Increasing the excitation current
d) Decreasing the load torque
Answer: c) Increasing the excitation current
Permanent magnet synchronous motor theory pdf | synchronous generators ion boldea pdf
91. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications that require:
a) High torque at low speeds
b) Variable speed control
c) High starting torque
d) Low power consumption
Answer: b) Variable speed control
92. The torque-angle characteristics of a synchronous motor are used to determine its:
a) Speed regulation
b) Power factor
c) Slip
d) Stability
Answer: d) Stability
93. Which of the following factors does not affect the synchronous speed of a motor?
a) Number of stator poles
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Number of rotor poles
d) Rated voltage of the motor
Answer: d) Rated voltage of the motor
94. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in large power generation plants?
a) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
b) Hysteresis synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) Reluctance synchronous motor
Answer: c) Salient pole synchronous motor
95. The field excitation in a synchronous motor is provided by:
a) Armature windings
b) Stator windings
c) Rotor windings
d) Field windings
Answer: d) Field windings
96. Which of the following is an advantage of a synchronous motor over an induction motor?
a) Higher starting torque
b) Lower cost
c) Variable speed control
d) Self-starting capability
Answer: c) Variable speed control
97. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications that require:
a) High torque at low speeds
b) Variable speed control
c) High starting torque
d) Low power consumption
Answer: b) Variable speed control
98. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be improved by:
a) Adding external resistance in the rotor circuit
b) Adjusting the number of stator windings
c) Increasing the excitation current
d) Decreasing the load torque
Answer: c) Increasing the excitation current
99. Which type of synchronous motor does not require any external excitation?
a) Salient pole synchronous motor
b) Hysteresis synchronous motor
c) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
d) Reluctance synchronous motor
Answer: c) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
100. The synchronous speed of a synchronous motor depends on:
a) The number of rotor poles
b) The number of stator poles
c) The supply frequency
d) The slip
Answer: b) The number of stator poles
101. Which component of a synchronous motor is responsible for providing mechanical power output?
a) Stator
b) Rotor
c) Armature windings
d) Field windings
Answer: b) Rotor
102. In a synchronous motor, the torque developed is directly proportional to:
a) The square of the stator current
b) The square of the rotor current
c) The product of the stator and rotor currents
d) The difference between the stator and rotor currents
Answer: c) The product of the stator and rotor currents
103. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications that require:
a) High starting torque
b) Precise speed control
c) Low power consumption
d) Variable speed operation
Answer: b) Precise speed control
104. Which of the following is a disadvantage of a permanent magnet synchronous motor?
a) High cost of permanent magnets
b) Limited operating temperature range
c) Low efficiency
d) Difficulties in controlling the speed
Answer: a) High cost of permanent magnets
105. The rotor of a synchronous motor rotates at:
a) The synchronous speed
b) A speed slightly higher than the synchronous speed
c) A speed slightly lower than the synchronous speed
d) The slip speed
Answer: a) The synchronous speed
106. The primary advantage of a synchronous motor over an induction motor is:
a) Higher efficiency
b) Lower cost
c) Higher torque
d) Precise speed control
Answer: d) Precise speed control
107. In a synchronous motor, the rotor locks in step with the rotating magnetic field due to:
a) Slip
b) Rotor resistance
c) Rotor inductance
d) Magnetic attraction
Answer: d) Magnetic attraction
108. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted by changing the:
a) Stator winding configuration
b) Rotor winding configuration
c) Excitation current
d) Rotor resistance
Answer: c) Excitation current
109. A synchronous motor operates at a speed equal to the:
a) Synchronous speed
b) Rotor speed
c) Slip speed
d) Stator speed
Answer: a) Synchronous speed
110. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in power systems for power factor correction?
a) Salient pole synchronous motor
b) Hysteresis synchronous motor
c) Reluctance synchronous motor
d) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
Answer: a) Salient pole synchronous motor
111. The torque developed by a synchronous motor is proportional to the:
a) Rotor resistance
b) Square of the stator current
c) Square of the rotor current
d) Product of the stator and rotor currents
Answer: d) Product of the stator and rotor currents
112. The field excitation of a synchronous motor is usually provided by:
a) Stator windings
b) Rotor windings
c) External DC source
d) Permanent magnets
Answer: c) External DC source
113. Synchronous motors are often used in applications that require:
a) High starting torque
b) Low maintenance
c) Variable speed control
d) Simple construction
Answer: c) Variable speed control
114. Which type of synchronous motor has a rotor made of a solid magnetic material?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Reluctance synchronous motor
c) Salient pole synchronous motor
d) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
Answer: a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
115. The armature winding of a synchronous motor is connected to:
a) DC power supply
b) Variable frequency power supply
c) Three-phase AC power supply
d) Single-phase AC power supply
Answer: c) Three-phase AC power supply
116. The field excitation in a synchronous motor is required to:
a) Generate torque
b) Start the motor
c) Provide cooling
d) Synchronize with the power supply
Answer: d) Synchronize with the power supply
117. Which of the following factors does not affect the synchronous speed of a synchronous motor?
a) Number of stator poles
b) Frequency of the power supply
c) Number of rotor poles
d) Stator winding resistance
Answer: d) Stator winding resistance
118. The power factor of a synchronous motor can be adjusted by changing the:
a) Rotor resistance
b) Stator resistance
c) Rotor reactance
d) Excitation current
Answer: d) Excitation current
119. Synchronous motors are often used in applications that require:
a) High starting torque
b) Variable speed control
c) Low power factor
d) Direct current supply
Answer: b) Variable speed control
120. The synchronous speed of a synchronous motor depends on:
a) The number of rotor poles
b) The number of stator poles
c) The slip
d) The rotor resistance
Answer: b) The number of stator poles
121. The field winding of a synchronous motor is usually connected to a:
a) DC power supply
b) AC power supply
c) Variable frequency power supply
d) Battery
Answer: a) DC power supply
122. Synchronous motors are commonly used in power systems for:
a) Voltage regulation
b) Current overload protection
c) Harmonic filtering
d) Phase balancing
Answer: a) Voltage regulation
123. The torque developed by a synchronous motor is proportional to the:
a) Stator current
b) Rotor current
c) Product of stator and rotor currents
d) Difference between stator and rotor currents
Answer: c) Product of stator and rotor currents
124. Which type of synchronous motor is commonly used in applications where high torque at low speeds is required?
a) Hysteresis synchronous motor
b) Salient pole synchronous motor
c) Reluctance synchronous motor
d) Permanent magnet synchronous motor
Answer: b) Salient pole synchronous motor
125. The primary disadvantage of a synchronous motor is:
a) High cost
b) Low efficiency
c) Limited speed control
d) Complex construction
Answer: a) High cost
For More Electrical Engineering Quiz Click Here