Statistics MCQs with Answers PDF Download Topic covering BCA Statistics subject. In This chapter are going to cover 5 units given below.
UNIT 1 BASICS OF STATISTICS AND STATISTICAL DATA,
UNIT 2 ANALYSIS OF STATISTICAL DATA,
UNIT 3 MEASURES OF STATISTICAL DATA,
UNIT 4 PERMUTATIONS, COMBINATIONS AND PROBABILITY,
UNIT 5 RANDOM VARIABLES AND DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS
UNIT 1 BASICS OF STATISTICS AND STATISTICAL DATA
Introduction To Statistics Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
- The specific statistical methods that can be used to summarize or to describe a collection of
data is called:
a) Descriptive statistics
b) Inferential statistics
c) Analytical statistics
d) All of the above
Ans. a
- The need for inferential statistical methods derives from the need for __.
a) Population
b) Association
c) Sampling
d) Probability
Ans. c
- A population, in statistical terms, is the totality of things under consideration. It is the
collection of all values of the _____ that is under study.
a) Instance
b) Variable
c) Amount
d) Measure - Non-sampling errors are introduced due to technically faulty observations or during the
__________ of data.
a) Processing
b) Analysis
c) Sequencing
d) Collection
Ans. a
- Sampling is simply a process of learning about the ______ on the basis of a
sample drawn from it.
a) Census
b) Population
c) Group
d) Area
Ans. b
- Numerical facts are usually subjected to statistical analysis with a view to helping a decision-
maker make wise decisions in the face of _______.
a)Interpreting
b) Uncertainty
c) Summarizing
d) Organizing
Ans. b
- In statistics, _______________ classification includes data according to the
time period in which the items under consideration occurred.
a) Chronological
b) Alphabetical
c) Geographical
d) Topological
Ans. a
- Data is simply the numerical results of any scientific__________________.
a) Analysis
b) Researches
c) Observation
d) Measurement
Ans. D
- The ____ process would be required to ensure that the data is complete and as
required.
a) Tabulation
b) Analysis
c) Editing
d) Ordering
Ans c
- A sample is a portion of the ____ population that is considered for study and
analysis.
a) Selected
b) Total
c) Fixed
d) Random
Ans. B
- The method of sampling, in which the choice of sample items depends exclusively on the
judgement of the investigator is termed as ____________.
a) Convenience sampling
b) Quota sampling
c) Systematic sampling d) Judgement sampling
Ans. d
- Both the sampling as well as the non-sampling errors must be reduced to a minimum in order
to get as representative a sample of the _______ as possible.
a) Group
b) Region
c) Population
d) Universe
Ans. c
- The larger the size of the population, the _______ should be the sample size.
a) Smaller
b) Larger
c) Accurate
d) Fixed
Ans. b
- When the data is to be processed by computers, then it must be coded and converted into the
________ _______.
a) English language
b) Regional language
c) Statistical language
d) Computer language
Ans. D
- A variable is any characteristic which can assume ________ values.
a) Different
b) Similar
c) Fixed
d) Assumed
Ans. A
- The basic objective of a sample is to draw ________ about the population
from which such sample is drawn.
a) Conclusion
b) Characteristics
c) Inferences
d) Parameters
Ans. C
- In _______ type of classification, the data is grouped together according to
some distinguished characteristic or attribute, such as religion, sex, age, national origin, and so
on.
a) Quantitative
b) Chronological c) Qualitative d) All of the above
Ans. C
To View Rest of the Content (MCQs) Please Join and Login for Membership
- A _________ variable is a variable whose values can theoretically take on an
infinite number of values within a given range of values.
a) Continuous
b) Discrete
c) Random
d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans. a
- A perfect random number table would be one in which every digit has been entered
___.
a) Chronologically
b) Sequentially
c) Randomly
d) Arbitrarily
Ans. C
- The _____ random variables yield categorical responses so that the responses
fit into one category or another.
a) Quantitative
b) Discrete
c) Continuous
d) Qualitative
Ans. d
- For a sample to be truly representative of the population, it must truly be________________.
a) Fixed
b) Random
c) Specific
d) Casual
Ans. b
- A __ __ is a phenomenon of interest in which the observed
outcomes of an activity are entirely by chance, are absolutely unpredictable and may differ from
response to response.
a) Discrete variable
b) Continuous variable
c) Random variable
d) All of the above
Ans. c
- By definition of randomness, each ____ __ has the same
chance of being considered.
a) Possible entity
b) Probable entity
c) Random entity
d) Observed entity
Ans A
- Before any procedures for _ _____ are established, the purpose
and the scope of the study must be clearly specified.
a) Data analysis
b) Data tabulation
c) Data collection
d) Data selection
Ans. C
- Adequacy of data is to be judged in the light of the requirements of the survey and the
geographical areas covered by the ______ data.
a) Collected
b) Available
c) Organized
d) Tabulated
Ans. b
- If the sample is truly representative of the population, then the characteristics of the sample
can be considered to be the same as those of the ___ population.
a) Fixed
b) Selected
c) Random
d) Entire
Ans. d
- Statistical inference deals with methods of inferring or drawing _______
about the characteristics of the population based upon the results of the sample taken from the
same population.
a) Details
b) Decisions
c) Conclusions
d) Samples
Ans. C
- If the sample size is too small, it may not ___ represent the population or the
universe as it is known, thus leading to incorrect inferences.
a) Appropriately
b) Reliably
c) Homogeneously d) Heterogeneously
Ans. A
- Editing would also help eliminate inconsistencies or obvious errors due to ___
treatment.
a) Characteristic
b) Arithmetical
c) Calculation
d) Tabulation
Ans. B
- When an investigator uses the data which has already been collected by others, such data is
called ___ _.
a) Primary data
b) Collected data
c) Processed data
d) Secondary data
Ans. D
- In the case of the questionnaire method of gathering data, it should be made certain that all
the questions have been _________.
a) Read
b) Interpreted
c) Answered
d) All of the above
Ans. c
- _________ provides various types of statistical information of either
qualitative or quantitative nature.
a) Sampling
b) Tabulation
c) Observation
d) Editing
Ans. A
- In statistics, ____________________classification groups the data according to locational
differences among the items.
a) Chronological
b) Geographical
c) Regional
d) Alphabetical
Ans. B
- The degree of randomness of selection would depend upon the process of selecting the items
from the ____________.
a) Population b) Region c) Sample d) Data
Ans. C
- A _________ sample is obtained by selecting convenient population units
a) Random
b) Quota
c) Stratified
d) Convenience
Ans. D
- A ______ sample is formed by selecting one unit at random and then selecting
additional units at evenly spaced intervals until the sample has been formed.
a) Stratified
b) Systematic
c) Judgement
d) Random
Ans . B
- The sampling errors arise due to drawing faulty inferences about the ______
based upon the results of the samples.
a) Sample
b) Survey
c) Population
d) Census
Ans C
- A summary measure that describes any given characteristic of the population is known as a
______.
a) Parameter
b) Information
c) Inference
d) Statistics
Ans. A
- ____ means separating items according to similar characteristics and grouping
them into various classes.
a) Tabulation
b) Editing
c) Separation
d) Classification
Ans. d
- _________ is one which is collected by the investigator himself for the
purpose of a specific inquiry or study.
a) Secondary data
b) Primary data
c) Statistical data
d) Published data
Ans. B
UNIT 2 ANALYSIS OF STATISTICAL DATA
Statistics MCQs PDF Download
- In chronological classification, the data is classified on the basis of:
a) Time
b) Money
c) Location
d) Quality
Ans. A
- The classification of data according to location is what classification:
a) Chronological
b) Quantitative
c) Qualitative
d) Geographical
Ans. D
- The magnitude of the class is the:
a) The product of lower limit and upper limit
b) The sum of lower limit and upper limit
c) The difference of upper limit and lower limit
d) None of these
Ans. C
- A function very similar to that of sorting letters in a post office is:
a) Mean
b) Standard deviation
c) Classification
d) Mean deviation
Ans. C
- The value lying half way between the upper limit and lower limit of the class is:
a) Class interval
b) Mid point c) Frequency d) None of the above
Ans. B
- The first step in tabulation is:
a) Foot note
b) Source note
c) Captions
d) Classification
Ans D
- A systematic arrangement of data in rows and columns is:
a) Table
b) Tabulation
c) Body
d) All the above
Ans A
- The numerical information in a statistical table is called the:
a) Table
b) Foot note
c) Source note
d) Body
Ans D
- In a statistical table the row headings are referred to as:
a) Source note
b) Captions
c) Stubs
d) Body
Ans. c
- In the statistical table column headings are called:
a) Stubs
b) Captions
c) Source note
d) None of these
Ans B
- If the class mid points in a frequency distribution of a group of persons are: 125, 132, 139,
146, 153, 160, 167, 174, 181 pounds, then the size of the class is:
a) 6 b) 8 c) 7 d) 9
Ans C
- The different types of samplings are:
a) Probability
b) Judgement
c) Mixed
d) All the above
Ans D
- Two dimensional diagrams used in surface diagrams are:
a) Squares
b) Pie diagrams
c) Circles
d) All the above
Ans D
- One dimensional diagram is:
a) Line diagram
b) Rectangles
c) Cubes
d) Squares
Ans A
- Type of bar diagram is:
a) Pictogram
b) Sub divided diagram
c) Line diagrams
d) Pie diagram
Ans B
- The most commonly used device of presenting business and economic data is:
a) Pie diagrams
b) Pictograms
c) Bar diagrams
d) Line diagrams
Ans C
- A pie diagram is also called:
a) Pictogram b) Angular diagram c) Line diagram d) Bar diagram
Ans B
- In volume diagram the three dimensions which are taken into account are:
a) Length, weight, breadth
b) Height, weight, breadth
c) Length, height, breadth
d) Length, weight, height
Ans C
- The median of a frequency distribution is found graphically with the help of:
a) Histogram
b) Frequency curve
c) Frequency polygon
d) Ogive
Ans d
- The mode of a frequency distribution can be determined graphically by:
a) Histogram
b) Frequency curve
c) Frequency polygon
d) Ogive
Ans A
- From the figure given in Question 27, find the only item that has shown positive growth
between 1991 and 1993?
a) Net fixed assets
b) Net current assets
c) Investments
d) Total assets
Ans C
- If a sample of size n from a given finite population of size N, then the total number of
samples is:
a) N! / (N –n)!
b) N!
c) N! /n!
d) N! /n! (N – n )!
Ans D
- The set of values of the statistic so obtained, one for each sample, constitutes what is called:
a) Sampling distribution
b) Systematic sampling
c) Stratified sampling
d) Cluster sampling
Ans A
- Standard error of the sampling distribution of a statistic t is:
a) √ Standard deviation
b) √Median
c) √Variance
d) √Mean
Ans C
- From the above graph in which year was the growth in expenditure maximum as compared
to the previous year:
a) 1993
b) 1995
c) 1991
d) 1992
Ans c
- From the above figure answer the retained profit in 1991-1992 as compared to that in 1990-
1991 was:
a) Higher by 2.5% b) Higher by 1.5% c) Lower by 2.5% d) Lower by 1.5%
Ans D
- Among every student what is the ratio of male and female:
a) 1:2
b) 2:1
c) 3:2
d) 2:3
Ans . D
- If the number of units of P is to be 3 times that of Q, what is the maximum idle time to
maximize total units manufactured?
a) 0 min
b) 24 min
c) 1 hr
d) 2 hr
Ans A
UNIT 3 MEASURES OF STATISTICAL DATA
Business Statistics MCQs with Answers pdf | Statistics MCQs with Answers pdf | Business Statistics MCQ pdf
- The standard deviation for 15, 22, 27, 11, 9, 21, 14, 9 is:
a) 6.22
b) 6.12
c) 6.04
d) 6.32
Ans. a
2. A student obtained the mean and the standard deviation of 100 observations as 40 and 5.1. It was later found that one observation was wrongly copied as 50, the correct figure being 40. Find the correct mean and the S.D.
a) Mean = 38.8, S.D =5
b) Mean = 39.9, S.D =5
c) Mean = 39.9, S.D = 4
d) None
Ans. b
3. The mean deviation about median from the data: 340, 150, 210, 240, 300, 310, 320 is:
a) 51.6
b) 51.8
c) 52
d) 52.8
Ans. d
4. For a frequency distribution mean deviation from mean is computed by
a) ∑E f /∑ E f |d|
b) ∑E d /∑Ef
c) ∑E fd/ ∑E f
d) ∑Ef | d | / ∑E f
Ans. d
5. The mean deviation from the median is:
a) Equal to that measured from another value
b) Maximum if all the observations are positive
c) Greater than that measured from any other value
d) Less than that measured from any value
Ans. d
6. The mean deviation of the series a, a + d, a +2d……., a + 2n from its mean is
a) (n + 1) d /2n +1
b) nd /2n +1
c) n (n +1) d /2n +1
d) (2n +1) d /n (n+1)
Ans. c
7. A batsman score runs in 10 innings as 38, 70, 48, 34, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54 and 44. The mean deviation about mean is
a) 8.6
b) 6.4
c) 10.6
d) 7.6
Ans. a
8. The arithmetic mean height of 50 students of a college is 5’—8’. The height of 30 of these is given in the frequency distribution. Find the arithmetic mean height of the remaining 20 students.
| Height in inches: Frequency: | 5’—- 4” 4 | 5’— 6” 12 | 5’ —- 8” 4 | 5’—-10” 8 | 6’ — 0” 2 |
| a) 5′—-8.8″ |
| b) 5’ —- 8.0” |
| c) 5’—– 7.8” |
| d) 5’—– 7.0” |
Ans. A
9. Find the sum of the deviation of the variable values 3, 4, 6, 8, 14 from their mean
a) 5
b) 0
c) 1
d) 7
Ans. d
10. The median of the observation 11, 12, 14, 18, x + 4, 30, 32, 35, 41 arranged in ascending order is 24, then x i
a) 21
b) 22
c) 23
d) 24
Ans. a
11. The median of the data: 19, 25, 59, 48, 35, 31, 30, 32, 51. If 25 is replaced by 52, what will be the new median.
a) 35
b) 53
c) 43
d) 45
Ans. a
12. If the median of the following frequency distribution is 46, find the missing frequencies.
| Variable: | 10—20 | 20—30 30—40 | 40—50 | 50—60 | 60—70 | 70—80 | Total |
| Frequency: | 12 | 30 a | 65 | b | 25 | 18 | 229 |
| a) a = 32 b =40 | |||||||
| b) a =31 b = 45 | |||||||
| c) a = 33 b = 42 | |||||||
| d) a =34 b =45 |
Ans. d
13. Find the value of x, if the mode of the data is 25: 15, 20, 25, 18, 14, 15, 25, 15, 18, 16, 20, 25, 20, x,
a) 15
b) 18
c) 25
d) 20
Ans. c
14. Compute the modal value for
x : 95 105 115 125 135 145 155 165 175
f : 4 2 18 22 21 19 10 3 2
a) 175
b) 125
c) 145
d) 165
Ans. b
15. Compute the mode for the following frequency distribution:
Size of items: 0-4 4-8 8-12 12-16 16-20 20-24 24-28 28-32 32-36 36-40
Frequency: 5 7 9 17 12 10 6 3 1 0
a) 32.66
b) 28.43
c) 24.87
d) 31.65
Ans. a
16. For the following grouped frequency distribution find the mode:
Class: 3-6 6-9 9-12 12-15 15-18 18-21 21-24
Frequency: 2 5 10 23 21 12 3
a) 13.9
b) 14.7
c) 15.1
d) 14.6
Ans. d
17. The table shows the age distribution of cases of a certain disease admitted during a year in a particular hospital.
Age (in years): 5-14 15-24 25-34 35-44 45-54 55-64
No of cases: 6 11 21 23 14 5
The average age for which maximum cases occurred is:
a) 34.33
b) 35.34
c) 36.31
d) 37.31
Ans. c
18. In a moderately symmetric distribution mean, median and mode are connected by:
a) Mode = 2 median – 3 mean
b) Mode = 3 median – 4 mean
c) Mode = 3 median – 2 mean
d) Mode = 2 median – 4 mean
Ans. c
21. The algebraic sum of the deviations of a set of n values from their mean is
a) 0
b) n – 1
c) n
d) n + 1
Ans. a
22. A,B, C are three sets of values of x:
A: 2, 3, 7, 1, 3, 2, 3
B: 7, 5, 9, 12, 5, 3, 8
C: 4, 4, 11, 7, 2, 3, 4
Which is true:
a) Mean of A = Mode of C
b) Mean of C = Median of B
c) Median of B = Mode of A
d) Mean, median, mode of A are equal
Ans. d
23. The mean and variance of 7 observations are 8 and 16 . If 5 of the observations are 2, 4, 10, 12, 14 the remaining 2 observations are:
a) x =6 , y = 8
b) x=5, y=7
c) x=7 , y=3
d) None of these
Ans. a
24. The variance of 15 observations is 4. If each observation is increased by 9, the variance of the resulting observation is:
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Ans. c
25. The mean of 5 observations is 4.4 and their variance is 8.24. If 3 of the observations are 1, 2, 6. The other 2 observations are:
a) 9, 4
b) 7, 8
c) 6, 5
d) 4, 8
Ans. a
26. The geometric mean of 10 observation s on a certain variable was calculated as 16.2. It was later discovered that one of the observations was wrongly recorded as 12.9; in fact it was 21.9. The correct G.M is:
a) 17.12
b) 18.43
c) 17.08
d) 18.15
Ans. c
27. Three groups of observations contain 8, 7 and 5 observations. Their geometric means are 8.52, 10.12 and 7.75. Find the geometric mean of the 20 observations in the single group formed by pooling the three groups is:
a) 7.831
b) 8.837
c) 9.643
d) 6.438
Ans.b
28. Find the Quartile deviation for the distribution:
Class Interval: 0 – 15 15 -30 30 – 45 45 – 60 60 – 75 75 – 90 90 – 105
f: 8 26 30 45 20 17 4
a) 15.44
b) 16.22
c) 14.55
d) 17.33
Ans. a
29. Find the quartile deviation for the data:
| Income (in Rs.): | Less than 50 | 50 -70 | 70 -90 | 90 – 110 | 110 -130 | 130 – 150 | Above150 |
| No of Persons: | 54 | 100 | 140 | 300 | 230 | 125 | 51 |
| a) 18.625 | |||||||
| b) 19.925 | |||||||
| c) 17.485 | |||||||
| d) None of these |
Ans. b
| 30. From the monthly income of 10 families find the coefficient of range is: | ||||||||||
| S. No: 1 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Income in (Rs.): 145 367 | 268 | 73 | 185 | 619 | 280 | 115 | 870 | 315 |
a) 0.1
b) 0.6
c) 0.84
d) 0.56
Ans. c
31. Find the value of third quartile if the values of first quartile and quartile deviation are 104 and 108 respectively.
a) 130
b) 140
c) 120
d) 110
Ans. b
32. Age distribution of 200 employees of a firm is given below and calculate semi inter quartile range = (Q3 – Q1 ) /2 of the distribution:
| Age in Years (less than): | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 |
| No of Employees: | 10 | 25 | 75 | 130 | 170 | 189 | 200 |
| a) 4.75 years | |||||||
| b) 4.25 years | |||||||
| c) 4 years | |||||||
| d) None of these |
Ans. a
33. Find the lower quartile for the distribution
Wages: 0 – 10 10 – 20 20 – 30 30 – 40 40 – 50
No of Workers: 22 38 46 35 20
a) 13.80
b) 12.56
c) 14.803
d) None of the above
Ans. c
34.Find the Mean deviation from the Mean for the following
Class Interval: 0 – 10 10 – 20 20 – 30 30 – 40 40 -50 50 – 60 60 – 70
Frequency: 8 12 10 8 3 2 7
a) 14
b) 12
c) 15
d) 16
Ans. d
35. Mean deviation which is calculated is minimum at:
a) Mean
b) Median
c) Mode
d) All the three
Ans. b
36. Initially there were 9 workers, all being paid a uniform wage. Later a 10th worker is added to the list whose wage rate is Rs. 20 less than for others. The standard deviations of wages for the group of 10 workers are:
a) 5
b)4
c)7
d) 6
Ans. d
37. Twenty passengers were found ticketless on a bus. The sum of squares and the standard deviation of the amount found in their pockets were Rs.2,000 and Rs.6. If the total fine imposed on these passengers is equal to the total amount recovered from them and fine imposed is uniform, what is the amount each one has to pay as fine?
a) 5
b) 6
c) 8
d) 9
Ans. c
38. For any discrete distribution standard deviation is not less than
a) Mean deviation from mean
b) Mean deviation from median
c) Mode
d) None of these
Ans. a
39. Mean of 10 items is 50 and S.D is 14. Find the sum of squares of all items
a) 26543
b) 26960
c) 27814
d) 27453
Ans. b
40. Find the range for the following data
14, 16, 16, 14, 22, 13, 15, 24, 12, 23, 14, 20, 17, 21, 22, 18, 18, 19, 20, 17, 16, 15, 11, 12, 21, 20,17, 18, 19, 23
a) 13
b) 12
c) 14
d) 16
Ans. a
UNIT 4 PERMUTATIONS, COMBINATIONS AND PROBABILITY
Permutation and Combination Problems with solutions and answers pdf | Probability mcq with answers pdf | Probability and Statistics mcqs with answers pdf | mcq on Probability Distribution with answers pdf |
- A five digit number is formed using digits 1,3 5, 7 and 9 without repeating any one of them. What is the sum of all such possible numbers?
a) 6666600
b) 6666660
c) 6666666
d) None of these
Ans. a
2. 139 persons have signed for an elimination tournament. All players are to be paired up for the first round, but because 139 is an odd number one player gets a bye, which promotes him to the second round, without actually playing in the first round. The pairing continues on the next round, with a bye to any player left over. If the schedule is planned so that a minimum number of matches is required to determine the champion, the number of matches which must be played is
a) 136
b) 137
c) 138
d) 139
Ans. c
3. A box contains 6 red balls, 7 green balls and 5 blue balls. Each ball is of different size. The probability that the red ball selected is the smallest red ball is
a) 1/8
b) 1/3
c) 1/6
d) 2/3
Ans. c
4.Boxes numbered 1,2,3,4 and 5 are kept in a row, and they which are to be filled with either a red ball or a blue ball, such that no two adjacent boxes can be filled with blue balls. Then how many different arrangements are possible, given that all balls of given colour are exactly identical in all respect?
a) 8
b) 10
c) 154
d) 22
Ans. d
5. For a scholarship, at the most n candidates out of 2n + 1 can be selected. If the number of different ways of selection of at least one candidate is 63, the maximum number of candidates that can be selected for the scholarship is
a) 3
b) 4
c) 6
d) 5
Ans. a
- Ten points are marked on a straight line and 11 points are marked on another straight line. How many triangles can be constructed with vertices from among the above points?
a) 495
b) 550
c) 1045
d) 2475
Ans. c
7. There are three cities A, B and C. Each of these cities is connected with the other two cities by at least one direct road. If a traveler wants to go from one city (origin) to another city (destination), she can do so either by traversing a road connecting the two cities directly, or by traversing two roads, the first connecting the origin to the third city and the second connecting the third city to the destination. In all, there are 33routes from A to B (including those via C), Similarly, there are 23 routes from B to C (including those via A). How many roads are there from A to C directly?
a) 6
b) 3
c) 5
d) 10
Ans. a
8. One red flag, three white flags and two blue flags are arranged in line such that
1 No two adjacent flags are of the same colour 2.The flags at the two ends of the line are of different colours.
In how many different ways the flag be arranged?
a) 6
b) 4
c) 10
d) 2
Ans. a
9. Each of the 11 letters A. H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X and Z appears same hen looked at in the mirror. They are called symmetric letters. Other letters in the alphabet are asymmetric letters. How many four letter computer passwords can be formed using only the symmetric letters ( no repetition allowed)
a) 7920
b) 330
c) 146.40
d) 419430
Ans. a
10. An intelligence agency forms a code of two distinct digits selected from 0, 1, 2,……, 9 such that the first digit of the code is non zero. The code, handwritten on the slip, can create confusion, when read upside down for example the code 91 can be read as 16. How many codes are there for which no such confusion can arise?
a) 80
b) 78
c) 71
d) 69
Ans. d
11. The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is known as
a) Permutation
b) Combination
c) Probability
d) Sample space
Ans. d
12. A card is drawn from a well shuffled pack of playing cards. Find the probability that it is either a diamond or a king
a) 4/26
b) 4/13
c) 17/52
d) 16/13
Ans. b
13. Let A and B be the two possible outcomes of an experiment and suppose P(A) = 0.4 P(AUB) =0.7 and P(B) =p. For what choice of p are A and B mutually exclusive?
a) 0.5
b) 0.2
c) 0.3
d) 0.6
Ans. c
14. Probability that a man will be alive 25 years hence is 0.3 and the probability that his wife will be alive 25 years hence is 0.4. Find the probability that 25 years hence only the man will be alive will be
a) 0.12
b) 0.18
c) 0.28
d) 0.42
Ans. b
15. A box of nine golf gloves contains two left-handed and seven right handed gloves. If three gloves are selected without replacement, what is the probability that all of them are left handed?
a) 1
b) 0
c) 7/18
d) 49/81
Ans. b
16. A lady declares that by taking a cup of tea, she can discriminate whether the milk or tea infusion was added to the cup. It is proposed to test this assertion by means of an experiment with 12 cups of tea, 6 made in one way and 6 in the other, and presenting them to the lady for judgement in a random order. The probability that on the null hypothesis that the lady has no discrimination power, she would judge correctly all the 12 cups, it being known to her that 6 are of each kind would be
a) 924
b) 1/925
c) 1/924
d) 925
Ans. c
17. A restaurant serves two special dishes A and B to its customers consisting of 60% men and 40% women. 80% of men order dish A and the rest B. 70% of women order B and the rest A. In what ratio of A to B should the restaurant prepare the two dishes?
a) 3:2
b) 2:3
c) 1:2
d) 2:1
Ans. a
18. A card is drawn at random from a well shuffled pack of cards. The probability that it is heart or a queen is
a) 4/13
b) 11/52
c) ½
d) 1/52
Ans. a
19. A piece of electronic equipment has two essential parts A and B. In the past, part A failed 30% of the times, part B failed 20% of the times and both failed simultaneously 5% of the times. Assuming that both parts must operate to enable the equipment to function, the probability that the equipment will function is
a) 0.1
b) 0.52
c) 0.55
d) 0.15
Ans. c
20. In a certain college, the students engage in sports in the following proportion Football (F): 60% of all students Basketball (B): 50% of all students. Both football and basketball: 30% of all students. If a student is selected at random the probability that he will play neither sports is
a) 0.8
b) 0.10
c) 0.7
d) 0.20
Ans. b
21. If P(A) =1/4, P(B) =2/5 and P(AUB) =1/2 find P(Ac U Bc ), where A and B are two non mutually exclusive events connected with a random experiment E and Ac is the complement event of A.
a) 0.85
b) 0.58
c) 0.80
d) 0.50
Ans. a
22. The result of an examination given to a class on three papers A, B and C are 40% failed in paper A, 30% failed in B, 25% failed in paper C, 15% failed in paper A and B both. 12% failed in B and C both, 10% failed in A and C both, 3% failed in A, B and C. What is the probability of a randomly selected candidates passing in all three papers?
a) 0.6
b) 0.39
c) 0.56
d) 0.42
Ans. b
23. The figure below shows the network of cities A, B, C, D, E and F. The arrows show the permissible direction of travel. What is the number of distinct paths from A to F?
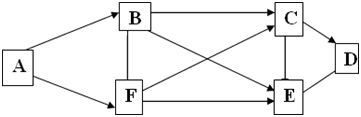
a) 9
b) 10
c) 11
d) None of these
Ans. b
24. Suppose it is 11 to 5 against a person who is now 38 years of age living till he is 73 and 5 to 3against B, now 43 living till he is 78. The chance that at least one of these persons will be alive 35 years hence is
a) 0.47
b) 0.57
c) 0.37
d) 0.67
Ans. b
25. The problem in Mathematics is given to three students A, B and C whose chances of solving it are 1/3, 1/4 and 1/2. The probability that the problem will be solved is
a) 1/12
b) 3/4
c) 7/12
d) None
Ans. b
26. If P(A) = 0.3 P(B) = 0.2 and P(C) =0.1 and A, B, C are independent events the probability of occurrence of at least one of the three events A,B, C is
a) 0.41
b) 0.37
c) 0.496
d) 0.387
Ans. c
27. A speaks the truth 3 times out of 4, and B 7 times out of 10; They both assert that a white ball has been drawn from a bag containing 6 balls of different colour. The truth in the assertion is
a) 35/36
b) 36/43
c) 25/36
d) 63/43
Ans. a
28. Three urns are given, each containing red and white balls. Urn 1: 6 red balls and 4 white, Urn 2: 2 red and 6 white, Urn3: 1 red and 8 white. An urn is chosen at random and a ball is drawn from this urn. The ball is red. The probability that the urn chosen was urn 1 is
a) 196/173
b) 173/196
c) 173/198
d) 198/173
Ans. d
29. A doctor is to visit a patient. The probability that he will come by car taxi scooter or by other means of transport are 0.3, 0.2, 0.1 and 0.4. The probabilities that he will be late are 1/4, 1/3 and ½, if he comes by car taxi and scooter. But if he comes by other means of transport he will not be late. When he arrives he is late. Therefore the probability that he comes by car are
a) 1/2
b) 0
c) 1/4
d) 1
Ans a
30. What is the chance that a leap year selected at random will contain 53 Sundays?
a) 2/7
b) 3/7
c) 1/7
d) 5/7
Ans. a
31. Out of all the 2-digit integers between 1 and 200, a 2- digit number has to be selected at random. What is the probability that the selected number is not divisible by 7?
a) 11/90
b) 33/90
c) 55/90
d) 77/90
Ans. d
32. Amarnath appears in an exam that has 4 subjects. The chance he passes an individual subject’s test is 0.8. The probability that he will pass in at least one of the subjects is
a) 0.99984
b) 0.9984
c) 0.0004
d) None of these
Ans. b
33. A box contains 2 tennis , 3 cricket and 4 squash balls. Three balls are drawn in succession with replacement. What is the probability that all are cricket balls:
a) 1/27
b) 2/27
c) 3/27
d) 1/9
Ans. a
34. In a garden 40% of the flowers are roses and the rest are carnations. If 25% of the roses and 10% of the carnations are red the probability that a red flower selected at random is a rose is
a) 5/8
b) 2/8
c) 7/8
d) 3/8
Ans. a
35. Three of the 6 vertices if a regular hexagon are chosen at random. The probability that the triangle with these vertices is equilateral is
a) 1/10
b) 4/10
c) 3/10
d) 1/5
Ans. a
36. What is the value of n(P(P(P(ø))))
a) 3 elements
b) 4 elements
c) 8 elements
d) 5 elements
Ans. b
37. In how many ways can 10 identical presents be distributed among 6 children so that each child gets at least one present ?
a) 15 C6
b) 16 C6
c) 9 C5
d) 610
Ans. c
38. There are 6 pups and 4 cats. In how many can they be seated in a row so that no cats sit together:
a) 6 ! 6 X 6 ! 6
b) 10!/4!6!
c) 6! X 7P4
d) 6!7!
Ans. c
39. There are V lines parallel to the X axis and W lines parallel to the Y axis. How many rectangles can be formed with the intersection of these lines?
a) vP2 .w P2
b) vC2 . w C2
c) vwC2
d) None of these
Ans. b
40. From 4 men and 4 women a committee of 5 is to be formed. Find the number of ways of doing so if the committee consists of a president, a vice president and three secretaries?
a) 720
b) 450
c) 1120
d) None of these
Ans. b
UNIT 5 RANDOM VARIABLES AND DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS
probability density function | binomial distribution | types of probability density function | use of probability density function | calculate binomial distribution
1.A die is thrown at random. What is the expectation of the number on it:
a) 3.7
b) 3.1
c) 3.5
d) 3.8
Ans. c
2. What is the expected number of heads appearing when a fair coin is tossed three times?
a) 2.1
b) 1.5
c) 3.2
d) 4.1
Ans. b
3. A contractor spends Rs. 3,000 to prepare for a bid on a construction project which, after deducting manufacturing expenses and the cost of bidding, will yield a profit of Rs. 25,000 if the bid is not won. If the chance of winning the bid is 10%, compute his expected profit?
a) 100
b) 607
c) 35
d) 200
Ans. d
4. Determine which of the following given values can serve as the values of a probability distribution of a random variable with the range x = 1, 2, 3 and 4
a) f(1) = 0.25 , f(2) = 0.75 , f(3) = 0.25 , f(4) = -0.25
b) f(1) = 0.15 , f(2) = 0.27 , f(3) = 0.29 , f(4) = 0.29
c) f(1) = 1/19 , f(2) = 10/19 , f(3) = 2/19 , f(4) = 5/19
d) None of these
Ans. b
5. For what values of k can f(x) = (1-k) kx
a) 0<k<1
b) k=0
c) k>1
d) None of these
Ans. a
6. From a bag containing 4 white and 6 red balls, three balls are drawn at random and if each white ball drawn carries a reward of Rs4 and each red ball Rs6, find the expected reward of the draw
a) Rs14.8
b) Rs15.6
c) Rs31
d) Rs16
Ans. b
7. A lot of 12 television sets include 2 with white chords. If 3 of the sets are chosen at random for shipment to the hotel, how many sets with white chords can the shipper expect to send to the hotel
a) 0
b) 1
c) 1/2
d) All of the above
Ans. c
8. E(x2) = 91/6. Find the value of E(2 x2+1) is
a) 92/3
b) 91/3
c) 90/3
d) 94/3
Ans. d
9. Given that X has the probability distribution f(x) = 1/8(3/x) for x = 0, 1, 2 and 3, find the moment-generating function of this random variable and use it to determine µ1`and µ2 `
a) 0
b) 3/2
c) 1/2
d) 1
Ans.b
10. For any random variable for which E(x) exists find the value of µ0
a) 0
b) -1
c) 2
d) 1
Ans. d
11. The moment-generating function of a random variable which has probability density f(x) = 1/2e-|x| for – ∞ < x < ∞ is
a) Mx (t) = 1/2t+1
b) Mx (t) = 1/1-t2
c) Mx (t) = 1/-2t
d) Mx (t) = 1/t2
Ans. b
12. Suppose an insurance company offers a 45 year old man a Rs1,000. 1 year term insurance policy for an annual premium of Rs12 . Assuming that the number of deaths per 1000 is 5 for persons in this age this group. The expected gain for the insurance company on a policy of this type is
a) 7
b) 8
c) 9
d) 10
Ans. a
13. In a business venture a man can make a profit of Rs 2,000 with probability of 0.4 or have a loss of Rs 1,000 with a probability of 0.6. His expected profit is
a) 100
b) 200
c) 400
d) 300
Ans. b
14. In a random throw of n dice, the expectation of the sum of points on them is
a) n/2
b) 3n/2
c) 7n/2
d) 9n/2
Ans. c
15. A number is chosen at random from the set 10.11,12- – -109; and another number is chosen at random from the set 12,13 ,14- – – 61. The expected value of their sum is
a) 95
b) 96
c) 97
d) 98
Ans. b
16. Three coins whose faces are marked 1 and 2 are tossed. Their expectations of the total values of numbers on their faces is
a) 9.5
b) 4.5
c) 3
d) 4
Ans. b
17. A and B throw with one die for a prize of Rs199 which is to be won by the player who first throws 6. If A has the first throw their respective expectation are
a) Rs 64, Rs 46
b) Rs 54, Rs 45
c) Rs 87, Rs 78
d) Rs 35, Rs 53
Ans. b
18. When 2 unbiased coins are tossed once, the variance of the number of head is
a) 1
b) 3/2
c) 1/4
d) None of these
Ans. d
19. A dice is tossed twice ‘getting a number less than 3’ is termed as success. Hence the mean of the number of successes is
a)1
b) 3/2
c) 1/4
d) 2/3
Ans. d
20. The expected value of X is usually written as:
a) E(X) or S
b) E(X) or µ
c) E(X) or j
d) E(X) or l
Ans. B
21. The probability distribution for
| x : | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | |
| p(x) : | 1/8 | 1/6 | 3/8 | ¼ | 1/12 |
The variance of the random variable x is
a) 20
b) 21
c) 22
d) 23
Ans. A


Comments are closed.