Multiple choice Questions of Botany Topic Organisms and Populations MCQs ( Organisms and Populations Quiz ) for NEET, GATE, AIAPGET, NEET MDS, NEET PG, DNB PDCET, AIIMS SS, PGIMER (Other), AIIMS PG and many more competitive examinations.
Organisms and Populations Important Questions | Multiple Choice Questions on Population
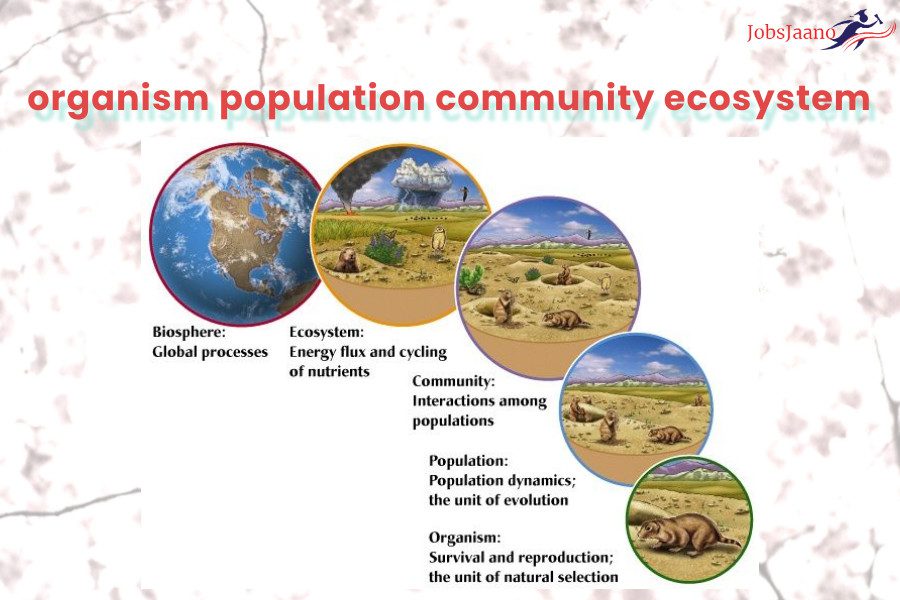
Important Questions of Organism, Population & their Community Multiple Choice Questions for NEET, UPSC, PPSC and all competitive examinations.
1. The relationship between species and another within community that has evolved through interaction is based upon
(a) requirement and mode of obtaining food only
(b) requirement and mode of obtaining shelter only
(c) on the habits of the species only
(d) All of the above
Ans. d
2. Communities that exist in the aphotic zone ultimately depend on food manufactured by the chemoautotrophic bacteria or
(a) algae and cyanobacteria that also live in the aphotic zone
(b) algae and cyanobacteria that live in the photic zone
(c) decomposers
(d) minerals found on the ocean bottom
Ans. b
3. An association of different inter-related populations belonging to different species in common environment. which can survive in nature is called
(a) herd
(b) family
(c) population
(d) community
Ans. d
4. Why is a new island more hospitable to the colonisers than an older island?
(a) Competition is more intense on the newer island
(b) Predation is loss of a factor on older islands
(c) The extinction rate is higher on the newer island
(d) The intensity of both competition and predation is less on the newer island
Ans. d
Species Population Community Ecosystem Biome Biosphere | Population and Community Ecology | Ecological Population
5. Which of the following is an omnivore?
(a) Man
(b) Crow
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Rat
Ans. c
6. Humans who have pets are healthier than humans, who do not have pets, which of these terms applies to the relationship between a human and a pet?
(a) Competition
(b) Parasitism
(c) Commensalism
(d) Mutualism
Ans. d
7. When the carrying capacity is equal to the population size, the net rate of increase in the population is equal to
(a) the carrying capacity
(b) less than zero
(c) the intrinsic rate of growth
(d) zero
Ans. d
8. The parasite, which come in contact with host for only a part of their life or occasionally at the time of feeding are called intermittent parasites. Which of the following is not an intermittent parasite?
(a) Leech
(b) Bed bug
(c) Female mosquito
(d) Ascaris
Ans. d
Organisms and Population NEET MCQ pdf
9. The animal, which captures and feeds on other animals is called
(a) predator
(b) prey
(c) parasite
(d) host
Ans. a
10. In world populations, individuals most often show a . pattern of dispersion.
(a) random
(b) density-dependent
(c) equilibrium
(d) clumped
Ans. d
11. Which of the following plants is not a predator plant?
(a) Hydrilla
(b) Drosera
(c) Utricularia
(d) Dionaea
Ans. a
12. The sum total of the populations of the same kind of organisms constitute
(a) colony
(b) genus
(c) community
(d) species
Ans. d
13. Intracellular endoparasite is
(a) Trichinella
(b) Plasmodium
(c) Trypanosoma
(d) Ascaris
Ans. b
14. A synthetic character of biotic community is
(a) fidelity
(b) dominance
(c) physiogamy
(d) All of these
Ans. d
MCQ on Population | Organism and Population mcq pdf | Multiple Choice Questions on Population Growth
15. Which one is a qualitative character?
(a) Abundance
(b) Frequency
(c) Biomass
(d) Phenology
Ans. d
16. A climax community is recognised by
(a) grasses, herbs and shrubs
(b) trees
(c) high biomass
(d) uniform composition
Ans. b
17. The phenomenon of having higher number of species in ecotone is called
(a) edge effect
(b) abundance
(c) frequency
(d) dominance effect
Ans. a
18. Wuchereria is a
(a) ectoparasite of man
(b) endoparasite of man
(c) predator of animals
(d) parasite of dog
Ans. b
19. What relationship persist between birds and cattle?
(a) Commensal
(b) Predator
(c) Protocooperation
(d) Mutualism
Ans. c
20. Female Anopheles visit the host for sucking blood at intervals. The type of parasitism is
(a) hemiparasite
(b) endoparasite
(c) holoparasite
(d) intermittent parasite
Ans. d
21. The type of relationship between sea anemone and hermit crab is
(a) commensalism
(b) mutualism
(c) symbiosis
(d) parasitism
Ans. b
22. Territory is defended against
(a) predator
(b) any intruder
(c) intruder of another species
(d) intruder of same species
Ans. b
Important Questions from Organisms and Populations | MCQ on Population Genetics | Population Ecology MCQ
23. Mycorrhiza, an association of fungus and angiospermic root is referred as
(a) ammensalism
(b) mutualism
(c) parasitism
(d) commensalism
Ans. b
24. The non-obligatory mutually beneficial relationship is represented by
(a) symbiosis
(b) protocooperation
(c) commensalism
(d) mimicry
Ans. b
25. Species interaction with negative influence on both is called
(a) predation
(b) parasitism
(c) ammensalism
(d) competition
Ans. d
26. An association of two species in which both species are benefitted is called
(a) protocooperation
(b) mutualism
(c) ammensalism
(d) All of these
Ans. b
27. Lichen is a symbiotic association of algae with
(a) protozoan
(b) fungi
(c) roots of plants
(d) bacteria
Ans. b
28. In aquatic mammals, a blubber is present
(a) in the skin
(b) around the different organs
(c) in the muscles
(d) in the connective tissue
Ans. d
29. The interdependent evolution of flowering plants and pollinating insects together is known as
(a) mutualism
(b) cooperation
(c) commensalism
(d) co-evolution
Ans. d
30. Exotic species sometimes become serious pest because of
(a) better environmental conditions in new locality
(b) better adaptability to new environment
(c) increase in reproductive potential
(d) the absence of natural competition
Ans. d
Question 1: Which of the following is a characteristic of a population?
A) Individual organisms
B) Abiotic factors
C) Biodiversity
D) Group of same species organisms
Answer: D) Group of same species organisms
Question 2: What term describes the variety of species in a particular ecosystem?
A) Population
B) Habitat
C) Biodiversity
D) Niche
Answer: C) Biodiversity
Question 3: Which of the following is an example of an abiotic factor?
A) Predation
B) Competition
C) Temperature
D) Disease
Answer: C) Temperature
Question 4: Which level of ecological organization includes all the living organisms in a particular area?
A) Population
B) Ecosystem
C) Community
D) Biosphere
Answer: C) Community
Question 5: What term describes the role a species plays in its ecosystem?
A) Population
B) Niche
C) Habitat
D) Ecosystem
Answer: B) Niche
Question 6: Which of the following is a biotic factor?
A) Sunlight
B) Water
C) Temperature
D) Plants
Answer: D) Plants
Question 7: Which of the following best defines carrying capacity?
A) The total number of species in an ecosystem
B) The maximum population size an environment can sustain
C) The rate of population growth in an area
D) The number of predator-prey interactions in a community
Answer: B) The maximum population size an environment can sustain
Question 8: Which of the following is an example of a density-independent factor affecting population size?
A) Predation
B) Disease
C) Food availability
D) Natural disasters
Answer: D) Natural disasters
Question 9: A group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time is called a:
A) Habitat
B) Ecosystem
C) Community
D) Population
Answer: D) Population
Question 10: The relationship between a predator and its prey is an example of:
A) Mutualism
B) Commensalism
C) Parasitism
D) Predation
Answer: D) Predation
Question 11: Which of the following is an example of a density-dependent factor that can influence population size?
A) Weather conditions
B) Natural disasters
C) Predation
D) Temperature
Answer: C) Predation
Question 12: The number of individuals in a population per unit area is known as:
A) Density
B) Dispersion
C) Diversity
D) Niche
Answer: A) Density
Question 13: Which of the following statements best describes an ecosystem?
A) A group of populations living in different areas
B) The interaction between abiotic and biotic factors in an area
C) A community of different species living together
D) The entire planet Earth
Answer: B) The interaction between abiotic and biotic factors in an area
Question 14: What is the term for the specific role or job that a species has in an ecosystem?
A) Biodiversity
B) Niche
C) Habitat
D) Population
Answer: B) Niche
Question 15: The process by which organisms with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce is called:
A) Natural selection
B) Genetic drift
C) Speciation
D) Hybridization
Answer: A) Natural selection
Question 16: Which of the following is an example of a primary consumer in a food chain?
A) Hawk
B) Grasshopper
C) Snake
D) Lion
Answer: B) Grasshopper
Question 17: Which of the following terms refers to a group of organisms of different species living together and interacting within an ecosystem?
A) Niche
B) Population
C) Community
D) Ecosystem
Answer: C) Community
Question 18: Which of the following best describes a keystone species in an ecosystem?
A) A species that is rare and endangered
B) A species that is a primary consumer in the food chain
C) A species that has a disproportionate impact on its ecosystem relative to its abundance
D) A species that is the largest predator in the ecosystem
Answer: C) A species that has a disproportionate impact on its ecosystem relative to its abundance
Question 19: The study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment is called:
A) Ecology
B) Evolution
C) Genetics
D) Physiology
Answer: A) Ecology
Question 20: Which of the following is an example of a r-selected species?
A) Elephant
B) Oak tree
C) Mouse
D) Lion
Answer: C) Mouse
Question 21: What term describes the variety of different ecosystems within a larger geographic area?
A) Biosphere
B) Habitat
C) Ecosystem
D) Biome
Answer: D) Biome
Question 22: Which of the following best describes the concept of mutualism?
A) One species benefits while the other is harmed
B) Both species benefit from the interaction
C) One species benefits at the expense of the other
D) Both species are unaffected by the interaction
Answer: B) Both species benefit from the interaction
Question 23: Which of the following is a measure of the total mass of living organisms within a given area?
A) Density
B) Biodiversity
C) Biomass
D) Abundance
Answer: C) Biomass
Question 24: What term describes the specific role that an organism plays within its community, including its interactions with other species and its habitat?
A) Niche
B) Population
C) Habitat
D) Community
Answer: A) Niche
Question 25: In a food chain, which trophic level includes organisms that consume both producers and other consumers?
A) Primary consumers
B) Secondary consumers
C) Tertiary consumers
D) Decomposers
Answer: B) Secondary consumers
Question 26: Which of the following is a factor that contributes to exponential population growth?
A) Limited resources
B) Predation
C) Carrying capacity
D) Rapid reproduction
Answer: D) Rapid reproduction
Question 27: Which of the following describes the movement of individuals out of a population and into other areas?
A) Immigration
B) Emigration
C) Migration
D) Dispersion
Answer: B) Emigration
Question 28: What term describes the range of conditions under which a species can survive and reproduce?
A) Niche
B) Ecosystem
C) Habitat
D) Tolerance range
Answer: D) Tolerance range
Question 29: What is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems?
A) Water
B) Wind
C) Sunlight
D) Soil
Answer: C) Sunlight
Question 30: Which of the following is an example of an abiotic factor in an ecosystem?
A) Predators
B) Plants
C) Temperature
D) Herbivores
Answer: C) Temperature
Question 31: What term describes the /multiple-choice-questions-on-food-processing-quality-control?
A) Predation
B) Commensalism
C) Mutualism
D) Competition
Answer: A) Predation
Question 32: Which of the following is an example of a density-independent factor affecting population growth?
A) Competition
B) Disease
C) Food availability
D) Hurricane
Answer: D) Hurricane
Question 33: Which type of population distribution is characterized by individuals being spaced evenly throughout their habitat?
A) Clumped
B) Random
C) Uniform
D) Dispersed
Answer: C) Uniform
Question 34: Which of the following is an example of a secondary consumer in a food chain?
A) Grasshopper
B) Deer
C) Rabbit
D) Hawk
Answer: D) Hawk
Question 35: What term describes the maximum rate at which a population could increase under ideal conditions?
A) Carrying capacity
B) Exponential growth
C) Birth rate
D) Biotic potential
Answer: D) Biotic potential
Question 36: Which type of population growth occurs when a population grows rapidly but then stabilizes at or near the carrying capacity?
A) Exponential growth
B) Logistic growth
C) Rapid growth
D) Boom-and-bust growth
Answer: B) Logistic growth
Question 37: What term describes the specific area where an organism lives and obtains its resources?
A) Niche
B) Ecosystem
C) Habitat
D) Community
Answer: C) Habitat
Question 38: The process of two different species evolving in response to each other over time is called:
A) Mutualism
B) Coevolution
C) Competition
D) Parasitism
Answer: B) Coevolution
Question 39: Which of the following best describes a pioneer species in ecological succession?
A) A species that is at the top of the food chain
B) A species that is rare and endangered
C) A species that is the largest in size
D) A species that is the first to colonize a barren area
Answer: D) A species that is the first to colonize a barren area
Question 40: Which of the following is a primary producer in an ecosystem?
A) Herbivore
B) Carnivore
C) Omnivore
D) Green plant
Answer: D) Green plant
Question 41: What term describes the process of individuals of the same species competing for limited resources?
A) Mutualism
B) Predation
C) Competition
D) Commensalism
Answer: C) Competition
Question 42: In a food web, which type of organism breaks down dead organic matter and recycles nutrients back into the ecosystem?
A) Primary producer
B) Primary consumer
C) Secondary consumer
D) Decomposer
Answer: D) Decomposer
Question 43: Which of the following best defines the term “ecosystem”?
A) A group of species living together in a specific area
B) A single organism and its environment
C) All living organisms on Earth
D) A community of organisms and their physical environment
Answer: D) A community of organisms and their physical environment
Question 44: Which of the following is an example of a negative feedback loop in population dynamics?
A) Increasing birth rates due to ample resources
B) Decreasing predation rates due to abundant prey
C) Decreasing birth rates due to overcrowding
D) Increasing predation rates due to declining prey
Answer: C) Decreasing birth rates due to overcrowding
Question 45: The process of a species adapting to its environment over generations is known as:
A) Immigration
B) Evolution
C) Emigration
D) Speciation
Answer: B) Evolution
Question 46: Which of the following is an example of a parasitic relationship?
A) Bees pollinating flowers
B) Lions hunting zebras
C) Humans farming crops
D) Fleas feeding on dogs
Answer: D) Fleas feeding on dogs
Question 47: Which of the following describes the gradual and predictable changes in species composition in an area over time?
A) Biodiversity
B) Speciation
C) Ecological succession
D) Genetic variation
Answer: C) Ecological succession
Question 48: Which of the following is a characteristic of a K-selected species?
A) Rapid reproduction
B) Short life span
C) Small body size
D) Few offspring with high parental investment
Answer: D) Few offspring with high parental investment
Question 49: Which of the following terms describes the total variety of species within an ecosystem?
A) Biomass
B) Population
C) Biodiversity
D) Niche
Answer: C) Biodiversity
Question 50: The interaction between two species where one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed is called:
A) Mutualism
B) Commensalism
C) Parasitism
D) Predation
Answer: B) Commensalism
Question 51: Which of the following is an example of an intrinsic factor affecting population growth?
A) Disease
B) Food availability
C) Birth rate
D) Temperature
Answer: C) Birth rate
Question 52: What term describes the specific physical location where an organism lives, feeds, and reproduces?
A) Niche
B) Habitat
C) Ecosystem
D) Biome
Answer: B) Habitat
Question 53: Which of the following is an example of a density-dependent factor affecting population growth?
A) Flood
B) Drought
C) Competition for resources
D) Earthquake
Answer: C) Competition for resources
Question 54: Which of the following is an example of a secondary succession?
A) Recovery after a forest fire
B) Establishment of pioneer species on bare rock
C) Establishment of grasses after a flood
D) Colonization of a newly formed volcanic island
Answer: A) Recovery after a forest fire
Question 55: The movement of energy and nutrients through living organisms within an ecosystem is known as:
A) Predation
B) Competition
C) Biotic exchange
D) Trophic transfer
Answer: D) Trophic transfer
Question 56: The term “niche partitioning” refers to:
A) The process of invasive species taking over a habitat
B) The competitive exclusion of one species by another
C) The division of resources and roles to reduce competition among species
D) The evolution of a species in response to a changing environment
Answer: C) The division of resources and roles to reduce competition among species
Question 57: Which of the following best defines the term “habitat”?
A) The role a species plays in its community
B) The specific area where an organism lives and obtains its resources
C) The variety of species within an ecosystem
D) The interaction between biotic and abiotic factors in an area
Answer: B) The specific area where an organism lives and obtains its resources
Question 58: What term describes the total number of different species in a given area?
A) Biomass
B) Population
C) Biodiversity
D) Niche
Answer: C) Biodiversity
Question 59: Which of the following describes a population that is growing exponentially without any limiting factors?
A) Carrying capacity
B) Boom-and-bust growth
C) Logistic growth
D) Exponential growth
Answer: D) Exponential growth
Question 60: The process by which organisms release stored energy from food is called:
A) Photosynthesis
B) Cellular respiration
C) Decomposition
D) Fermentation
Answer: B) Cellular respiration
Question 61: Which of the following is an example of a keystone species?
A) Grass
B) Rabbit
C) Wolf
D) Mouse
Answer: C) Wolf
Question 62: Which of the following terms describes a relationship between two species where one benefits and the other is harmed?
A) Mutualism
B) Commensalism
C) Parasitism
D) Predation
Answer: C) Parasitism
Question 63: The range of conditions in which a species can survive and reproduce is referred to as:
A) Niche
B) Habitat
C) Ecosystem
D) Tolerance range
Answer: D) Tolerance range
Question 64: Which of the following is an example of an ectothermic organism?
A) Human
B) Bear
C) Bird
D) Lizard
Answer: D) Lizard
Question 65: Which of the following describes the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
A) To produce food through photosynthesis
B) To provide energy to the primary consumers
C) To break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients
D) To control predator populations
Answer: C) To break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients
Question 66: The study of the interactions between living organisms and their environment is called:
A) Biology
B) Ecology
C) Genetics
D) Physiology
Answer: B) Ecology
Question 67: Which of the following terms describes the movement of individuals into a population from other areas?
A) Immigration
B) Emigration
C) Migration
D) Dispersion
Answer: A) Immigration
Question 68: Which of the following is an example of a climax community?
A) Newly formed volcanic island
B) Recovering after a forest fire
C) A mature and stable forest ecosystem
D) A deforested area with pioneer species
Answer: C) A mature and stable forest ecosystem
Question 69: Which of the following is an example of a density-independent factor affecting population size?
A) Competition for resources
B) Disease
C) Predation
D) Availability of mates
Answer: B) Disease
Question 70: The process by which new species arise due to the accumulation of small genetic changes over long periods of time is known as:
A) Natural selection
B) Speciation
C) Symbiosis
D) Migration
Answer: B) Speciation
Question 71: Which of the following best describes a biome?
A) A group of different species interacting within an ecosystem
B) A specific area where a species lives and obtains its resources
C) A large geographic region with similar climatic conditions and vegetation
D) The maximum population size that an environment can sustain
Answer: C) A large geographic region with similar climatic conditions and vegetation
Question 72: In a food web, which organisms are responsible for converting solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis?
A) Primary consumers
B) Secondary consumers
C) Tertiary consumers
D) Producers
Answer: D) Producers
Question 73: Which of the following is an example of a density-dependent factor affecting population size?
A) Flood
B) Fire
C) Earthquake
D) Competition for food
Answer: D) Competition for food
Question 74: Which of the following is an example of an omnivore?
A) Lion
B) Hawk
C) Grasshopper
D) Bear
Answer: D) Bear
Question 75: What term describes the gradual replacement of one type of community by another in an area over time?
A) Evolution
B) Adaptation
C) Succession
D) Competition
Answer: C) Succession
What is the term for a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area?
A) Ecosystem
B) Community
C) Population
D) Habitat
Answer: C) Population
Which of the following is a biotic factor in an ecosystem?
A) Sunlight
B) Temperature
C) Soil pH
D) Plants
Answer: D) Plants
Which of the following is an abiotic factor in an ecosystem?
A) Bacteria
B) Birds
C) Rainfall
D) Fish
Answer: C) Rainfall
The study of the interactions between different species in a community is called:
A) Population dynamics
B) Ecosystem ecology
C) Community ecology
D) Behavioral ecology
Answer: C) Community ecology
What is the maximum number of offspring that a species can produce under ideal environmental conditions called?
A) Carrying capacity
B) Population density
C) Reproductive potential
D) Limiting factor
Answer: C) Reproductive potential
Which of the following describes the range of conditions that an organism can tolerate and survive in?
A) Habitat
B) Niche
C) Ecosystem
D) Tolerance range
Answer: D) Tolerance range
The concept that two species cannot occupy the same ecological niche in the same habitat for an extended period is known as:
A) Competitive exclusion principle
B) Mutualism
C) Commensalism
D) Symbiosis
Answer: A) Competitive exclusion principle
What is the term for the total number of different species in a specific area or habitat?
A) Population density
B) Biodiversity
C) Reproductive potential
D) Carrying capacity
Answer: B) Biodiversity
Which of the following is an example of a density-dependent factor that can limit population growth?
A) Weather conditions
B) Predation
C) Earthquakes
D) Availability of food
Answer: D) Availability of food
When a population grows rapidly and exceeds the carrying capacity of its environment, what is likely to happen?
A) The population will stabilize at the carrying capacity
B) The population will decrease in size
C) The population will migrate to a new habitat
D) The carrying capacity will increase to accommodate the population
Answer: B) The population will decrease in size
Which of the following factors does NOT contribute to the exponential growth of a population?
A) High birth rate
B) Low death rate
C) Limited resources
D) No predators
Answer: C) Limited resources
What is the term for the variety of different species in a specific ecosystem or on Earth as a whole
A) Population density
B) Niche diversity
C) Genetic diversity
D) Species richness
Answer: C) Genetic diversity
In a food chain, which trophic level contains primary producers?
A) Primary consumers
B) Secondary consumers
C) Tertiary consumers
D) Producers
Answer: D) Producers
Which of the following is an example of a density-independent factor that can affect a population?
A) Competition for resources
B) Predation
C) Disease outbreak
D) Drought
Answer: D) Drought
What is the term for the total mass of living organisms in a given area or ecosystem?
A) Biomass
B) Population density
C) Carrying capacity
D) Niche
Answer: A) Biomass
Which of the following is NOT a type of symbiotic relationship?
A) Mutualism
B) Predation
C) Commensalism
D) Parasitism
Answer: B) Predation
When a population size remains relatively stable over time, it is said to be in:
A) Exponential growth
B) Logistic growth
C) Carrying capacity
D) Decline
Answer: B) Logistic growth
The process by which one organism captures and consumes another organism for food is known as:
A) Competition
B) Symbiosis
C) Predation
D) Mutualism
Answer: C) Predation
Which of the following is an example of a pioneer species?
A) Oaktree
B) Moss
C) Rabbit
D) Lion
Answer: B) Moss
What is the term for the role an organism plays in its ecosystem, including its interactions with other species?
A) Habitat
B) Niche
C) Territory
D) Population
Answer: B) Niche
Which of the following is a density-dependent factor that can regulate a population?
A) Earthquakes
B) Disease outbreak
C) Temperature
D) Sunlight
Answer: B) Disease outbreak
Which of the following best describes the carrying capacity of an environment?
A) The maximum number of species in an ecosystem
B) The total number of individuals in a population
C) The maximum population size an environment can sustain
D) The rate at which a population grows
Answer: C) The maximum population size an environment can sustain
In a population pyramid, what does a wide base represent?
A) Rapid population growth
B) Stable population size
C) Declining population
D) High death rate
Answer: A) Rapid population growth
Which of the following is an example of a density-dependent limiting factor?
A) Earthquake
B) Availability of water
C) Forest fire
D) Temperature
Answer: B) Availability of water
What is the term for the movement of individuals in and out of a population?
A) Immigration
B) Emigration
C) Birth rate
D) Death rate
Answer: A) Immigration
Which type of survivorship curve is characterized by high survivorship throughout most of the lifespan and then a rapid decline in old age?
A) Type I
B) Type II
C) Type III
D) Type IV
Answer: A) Type I
What is the term for the maximum population size that a habitat or environment can support indefinitely?
A) Population density
B) Carrying capacity
C) Exponential growth
D) Biotic potential
Answer: B) Carrying capacity
Which of the following is an example of a keystone species?
A) Ants
B) Grasshoppers
C) Bees
D) Sea otters
Answer: D) Sea otters
What is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems on Earth?
A) Wind
B) Sunlight
C) Geothermal energy
D) Fossil fuels
Answer: B) Sunlight
Which of the following best describes a population’s age structure?
A) The number of males and females in a population
B) The distribution of individuals in different age groups within a population
C) The number of individuals that emigrate from a population
D) The number of individuals that immigrate into a population
Answer: B) The distribution of individuals in different age groups within a population
Which of the following factors is most likely to result in a decrease in a population’s size?
A) Increased birth rate
B) Decreased death rate
C) Emigration
D) Abundant food supply
Answer: C) Emigration
What term is used to describe the total number of different species in a specific area or habitat?
A) Genetic diversity
B) Species richness
C) Habitat diversity
D) Ecosystem diversity
Answer: B) Species richness
The process by which organisms gradually change over time in response to their environment is known as:
A) Evolution
B) Symbiosis
C) Competition
D) Predation
Answer: A) Evolution
Which of the following best describes a climax community in ecology?
A) A community that is stable and not subject to change
B) A community at its earliest stage of development
C) A community that experiences constant disturbances
D) A community with very low biodiversity
Answer: A) A community that is stable and not subject to change
What type of survivorship curve is characterized by a relatively constant death rate throughout the lifespan of an organism?
A) Type I
B) Type II
C) Type III
D) Type IV
Answer: B) Type II
In a population, what does the term “density-dependent” mean?
A) Factors that affect the population’s density
B) Factors that are unrelated to population density
C) Factors that limit population growth regardless of density
D) Factors that only apply to small populations
Answer: A) Factors that affect the population’s density
Which of the following is a biotic factor that can limit a population’s size?
A) Temperature
B) Soil pH
C) Predation
D) Sunlight intensity
Answer: C) Predation
What type of relationship exists when two species benefit from their interaction with each other?
A) Competition
B) Parasitism
C) Mutualism
D) Commensalism
Answer: C) Mutualism
Which of the following is a density-independent factor that can affect population growth?
A) Competition for resources
B) Disease outbreak
C) Temperature extremes
D) Predation pressure
Answer: C) Temperature extremes
Which of the following is NOT an example of a primary consumer in a food chain?
A) Herbivorous insects
B) Deer
C) Carnivorous birds
D) Grazing cattle
Answer: C) Carnivorous birds
Which of the following best represents exponential population growth?
A) J-shaped growth curve
B) S-shaped growth curve
C) Steady linear growth curve
D) Declining growth curve
Answer: A) J-shaped growth curve
What is the primary source of nitrogen in most ecosystems?
A) Atmosphere
B) Soil minerals
C) Decomposing organic matter
D) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Answer: A) Atmosphere
What is the term for the maximum number of individuals of a species that an ecosystem can support without being degraded over the long term?
A) Carrying capacity
B) Reproductive potential
C) Logistic growth
D) Exponential growth
Answer: A) Carrying capacity
Which of the following describes a generalist species?
A) A species with a narrow ecological niche
B) A species with a limited diet
C) A species that can thrive in a wide range of habitats and feed on a variety of foods
D) A species that is highly specialized for a specific environment
Answer: C) A species that can thrive in a wide range of habitats and feed on a variety of foods
What term is used to describe the study of the movement and distribution of organisms in relation to their environment?
A) Ecology
B) Biogeography
C) Genetics
D) Taxonomy
Answer: B) Biogeography
Which of the following is a type of interspecific interaction where one organism benefits, and the other is neither helped nor harmed?
A) Mutualism
B) Parasitism
C) Commensalism
D) Predation
Answer: C) Commensalism
What is the term for the process of two different species evolving in response to each other over time?
A) Coevolution
B) Convergent evolution
C) Adaptive radiation
D) Speciation
Answer: A) Coevolution
Which of the following factors contributes to the uneven distribution of species around the world?
A) Ocean currents
B) Solar radiation
C) Continental drift
D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above
What is the term for the specific role or job that an organism has within its ecosystem?
A) Habitat
B) Niche
C) Territory
D) Domain
Answer: B) Niche
Which of the following best describes the concept of “ecological succession”?
A) The seasonal migration of animals
B) The replacement of one community of organisms by another over time
C) The process of competition between species
D) The movement of individuals in and out of a population
Answer: B) The replacement of one community of organisms by another over time
In ecological terms, what does the term “resilience” refer to?
A) The ability of a population to reproduce rapidly
B) The ability of an ecosystem to recover from disturbances
C) The maximum growth rate of a species
D) The variety of species in an ecosystem
Answer: B) The ability of an ecosystem to recover from disturbances
Which of the following is an example of an invasive species?
A) A native bird species
B) A plant species introduced from another country that disrupts local ecosystems
C) An endangered species
D) A keystone species
Answer: B) A plant species introduced from another country that disrupts local ecosystems
What is the term for the process by which individuals with advantageous traits survive and reproduce, leading to changes in the characteristics of a population over time?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Artificial selection
D) Genetic mutation
Answer: B) Natural selection
Which of the following is a biotic factor that can limit population growth?
A) Rainfall
B) Soil composition
C) Disease
D) Temperature
Answer: C) Disease
What is the primary source of energy for the majority of ecosystems on Earth?
A) Geothermal energy
B) Wind
C) Sunlight
D) Fossil fuels
Answer: C) Sunlight
Which of the following is an example of a secondary consumer in a food chain?
A) Grasshopper
B) Snake
C) Earthworm
D) Algae
Answer: B) Snake
In a population, what does the term “emigration” refer to?
A) The number of births in the population
B) The number of deaths in the population
C) The movement of individuals out of the population
D) The movement of individuals into the population
Answer: C) The movement of individuals out of the population
Which of the following describes a K-selected species?
A) A species that produces many offspring with little parental care
B) A species that has a high reproductive rate
C) A species that lives in unstable environments
D) A species that invests heavily in a few offspring with extensive parental care
Answer: D) A species that invests heavily in a few offspring with extensive parental care
What term is used to describe the process by which a community gradually changes over time, following a disturbance?
A) Ecological succession
B) Habitat fragmentation
C) Genetic drift
D) Biogeography
Answer: A) Ecological succession
Which of the following is an example of a niche overlap?
A) Two species of birds that feed on different types of insects in the same tree
B) A lion and a hyena competing for the same prey
C) A snake and a mongoose living in the same burrow
D) A tree and a vine growing side by side in a forest
Answer: A) Two species of birds that feed on different types of insects in the same tree
For More Topic Wise Botany MCQs CLICK HERE
For Zoology MCQs CLICK HERE
For Environment and Ecology MCQs Click Here